The molecular pathogenesis of triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 36091841
- PMCID: PMC9449346
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.979307
The molecular pathogenesis of triptolide-induced hepatotoxicity
Abstract
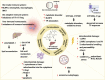
Triptolide (TP) is the major pharmacologically active ingredient and toxic component of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. However, its clinical potential is limited by a narrow therapeutic window and multiple organ toxicity, especially hepatotoxicity. Furthermore, TP-induced hepatotoxicity shows significant inter-individual variability. Over the past few decades, research has been devoted to the study of TP-induced hepatotoxicity and its mechanism. In this review, we summarized the mechanism of TP-induced hepatotoxicity. Studies have demonstrated that TP-induced hepatotoxicity is associated with CYP450s, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), oxidative stress, excessive autophagy, apoptosis, metabolic disorders, immunity, and the gut microbiota. These new findings provide a comprehensive understanding of TP-induced hepatotoxicity and detoxification.
Keywords: CYP450s; hepatotoxicity; immunity; oxidative stress; triptolide.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Wu, Wang, Zhang, Liu, Zhou and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

