Taro raphide-associated proteins: Allergens and crystal growth
- PMID: 36091877
- PMCID: PMC9440338
- DOI: 10.1002/pld3.443
Taro raphide-associated proteins: Allergens and crystal growth
Abstract
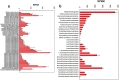
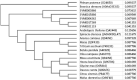
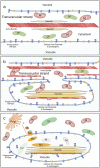
Calcium oxalate raphide crystals are found in bundles in intravacuolar membrane chambers of specialized idioblasts cells of most plant families. Aroid raphides are proposed to cause acridity in crops such as taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott). Acridity is irritation that causes itchiness and pain when raw/insufficiently cooked tissues are eaten. Since raphides do not always cause acridity and since acridity can be inactivated by cooking and/or protease treatment, it is possible that a toxin or allergen-like compound is associated with the crystals. Using two-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry (MS) peptide sequencing of selected peptides from purified raphides and taro apex transcriptome sequencing, we showed the presence on the raphides of peptides normally associated with mitochrondria (ATP synthase), chloroplasts (chaperonin ~60 kDa), cytoplasm (actin, profilin), and vacuole (V-type ATPase) that indicates a multistage biocrystallation process ending with possible invagination of the tonoplast and addition of mucilage that may be derived from the Golgi. Actin might play a crucial role in the generation of the needle-like raphides. One of the five raphide profilins genes was highly expressed in the apex and had a 17-amino acid insert that significantly increased that profilin's antigenic epitope peak. A second profilin had a 2-amino acid insert and also had a greater B-cell epitope prediction. Taro profilins showed 83% to 92% similarity to known characterized profilins. Further, commercial allergen test strips for hazelnuts, where profilin is a secondary allergen, have potential for screening in a taro germplasm to reduce acridity and during food processing to avoid overcooking.
Keywords: actin; biomineralization; calcium oxalate; crystalloplastids; profilin; transvacuolar strands.
© 2022 The Authors. Plant Direct published by American Society of Plant Biologists and the Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Akpan, E. J. , & Umoh, I. B. (2004). Effect of heat and tetracycline treatments of the food quality and acridity factors in cocoyam (Xanthosoma sagittifolium (l) Schott). Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, 3, 240–243.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

