Classification of breast cancer using a manta-ray foraging optimized transfer learning framework
- PMID: 36092017
- PMCID: PMC9454783
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1054
Classification of breast cancer using a manta-ray foraging optimized transfer learning framework
Abstract
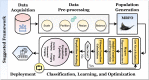
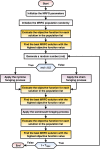
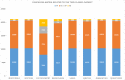
Due to its high prevalence and wide dissemination, breast cancer is a particularly dangerous disease. Breast cancer survival chances can be improved by early detection and diagnosis. For medical image analyzers, diagnosing is tough, time-consuming, routine, and repetitive. Medical image analysis could be a useful method for detecting such a disease. Recently, artificial intelligence technology has been utilized to help radiologists identify breast cancer more rapidly and reliably. Convolutional neural networks, among other technologies, are promising medical image recognition and classification tools. This study proposes a framework for automatic and reliable breast cancer classification based on histological and ultrasound data. The system is built on CNN and employs transfer learning technology and metaheuristic optimization. The Manta Ray Foraging Optimization (MRFO) approach is deployed to improve the framework's adaptability. Using the Breast Cancer Dataset (two classes) and the Breast Ultrasound Dataset (three-classes), eight modern pre-trained CNN architectures are examined to apply the transfer learning technique. The framework uses MRFO to improve the performance of CNN architectures by optimizing their hyperparameters. Extensive experiments have recorded performance parameters, including accuracy, AUC, precision, F1-score, sensitivity, dice, recall, IoU, and cosine similarity. The proposed framework scored 97.73% on histopathological data and 99.01% on ultrasound data in terms of accuracy. The experimental results show that the proposed framework is superior to other state-of-the-art approaches in the literature review.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Convolutional neural network (CNN); Deep learning (DL); Manta-Ray foraging algorithm (MRFO); Metaheuristic optimization.
©2022 N Baghdadi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An optimized transfer learning-based approach for automatic diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021 May 27;7:e555. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.555. eCollection 2021. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2021. PMID: 34141886 Free PMC article.
-
A multimodal AI-based non-invasive COVID-19 grading framework powered by deep learning, manta ray, and fuzzy inference system from multimedia vital signs.Heliyon. 2023 Jun;9(6):e16552. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16552. Epub 2023 May 25. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37251492 Free PMC article.
-
An automated diagnosis and classification of COVID-19 from chest CT images using a transfer learning-based convolutional neural network.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105383. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105383. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35290811 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis: A comprehensive review of pre-trained deep learning models based on feature extraction algorithm.Results Eng. 2023 Jun;18:101020. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101020. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Results Eng. 2023. PMID: 36945336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Challenge of Deep Learning for the Prevention and Automatic Diagnosis of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 23;14(24):2896. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14242896. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SNSVM: SqueezeNet-Guided SVM for Breast Cancer Diagnosis.Comput Mater Contin. 2023 Aug 30;76(2):2201-2216. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2023.041191. Comput Mater Contin. 2023. PMID: 38559807 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced object detection in remote sensing images by applying metaheuristic and hybrid metaheuristic optimizers to YOLOv7 and YOLOv8.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 28;15(1):7226. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89124-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40021716 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Detection via Multi-Tiered Self-Contrastive Learning in Microwave Radiometric Imaging.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 25;15(5):549. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15050549. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075796 Free PMC article.
-
Transformative Approaches in Breast Cancer Detection: Integrating Transformers into Computer-Aided Diagnosis for Histopathological Classification.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;12(3):212. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12030212. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150677 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy Analysis of Deep Learning Methods in Breast Cancer Classification: A Structured Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 11;13(4):683. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13040683. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abualigah L, Elaziz MA, Khasawneh AM, Alshinwan M, Ibrahim RA, Al-qaness MA, Mirjalili S, Sumari P, Gandomi AH. Meta-heuristic optimization algorithms for solving real-world mechanical engineering design problems: a comprehensive survey, applications, comparative analysis, and results. Neural Computing and Applications. 2022;34:4081–4110. doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-06747-4. - DOI
-
- Agarwal N, Sondhi A, Chopra K, Singh G. Transfer learning: survey and classification. In: Tiwari S, Trivedi M, Mishra K, Misra A, Kumar K, Suryani E, editors. Smart innovations in communication and computational sciences. vol. 1168. Springer; Singapore: 2021. (Advances in intelligent systems and computing). - DOI
-
- Alshinwan M, Abualigah L, Shehab M, Elaziz MA, Khasawneh AM, Alabool H, Hamad HA. Dragonfly algorithm: a comprehensive survey of its results, variants, and applications. Multimedia Tools and Applications. 2021;80(10):14979–15016. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-10255-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
