Neuroprotective Effect and Possible Mechanisms of Ginsenoside-Rd for Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Damage in Experimental Animal: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
- PMID: 36092162
- PMCID: PMC9458376
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7650438
Neuroprotective Effect and Possible Mechanisms of Ginsenoside-Rd for Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Damage in Experimental Animal: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Abstract
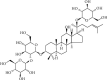
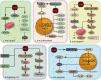
Ischemic stroke, the most common type of stroke, can lead to a long-term disability with the limitation of effective therapeutic approaches. Ginsenoside-Rd (G-Rd) has been found as a neuroprotective agent. In order to investigate and discuss the neuroprotective function and underlying mechanism of G-Rd in experimental animal models following cerebral ischemic/reperfusion (I/R) injury, PubMed, Embase, SinoMed, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure were searched from their inception dates to May 2022, with no language restriction. Studies that G-Rd was used to treat cerebral I/R damage in vivo were selected. A total of 18 articles were included in this paper, and it was showed that after cerebral I/R damage, G-Rd administration could significantly attenuate infarct volume (19 studies, SMD = -1.75 [-2.21 to - 1.30], P < 0.00001). Subgroup analysis concluded that G-Rd at the moderate doses of >10- <50 mg/kg reduced the infarct volume to the greatest extent, and increasing the dose beyond 50 mg/kg did not produce better results. The neuroprotective effect of G-Rd was not affected by other factors, such as the animal species, the order of administration, and the ischemia time. In comparison with the control group, G-Rd administration could improve neurological recovery (lower score means better recovery: 14 studies, SMD = -1.50 [-2.00 to - 1.00], P < 0.00001; higher score means better recovery: 8 studies, SMD = 1.57 [0.93 to 2.21], P < 0.00001). In addition, this review suggested that G-Rd in vivo can antagonize the reduced oxidative stress, regulate Ca2+, and inhibit inflammatory, resistance to apoptosis, and antipyroptosis on cerebral I/R damage. Collectively, G-Rd is a promising natural neuroprotective agent on cerebral I/R injury with unique advantages and a clear mechanism of action. More clinical randomized, blind-controlled trials are also needed to confirm the neuroprotective effect of G-Rd on cerebral I/R injury.
Copyright © 2022 Ai-fang Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

