Fixed Beamline Optimization for Intensity Modulated Carbon-Ion Therapy
- PMID: 36092271
- PMCID: PMC9457306
- DOI: 10.1109/trpms.2021.3092296
Fixed Beamline Optimization for Intensity Modulated Carbon-Ion Therapy
Abstract
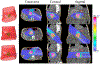
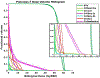
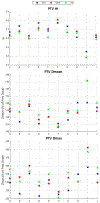
A major obstacle for the adoption of heavy ion therapy is the cost and technical difficulties to construct and maintain a rotational gantry. Many heavy ion treatment facilities instead choose to construct fixed beamlines as a compromise, which we propose to mitigate with optimized treatment couch angle. We formulate the integrated beam orientation and scanning spot optimization problem as a quadratic cost function with a group sparsity regularization term. The optimization problem is efficiently solved using fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm (FISTA). To test the method, we created the fixed beamline plans with couch rotation (FBCR) and without couch rotation (FB) for intensity modulated carbon-ion therapy (IMCT) and compared with the ideal scenario where both the couch and gantry have 360 degrees of freedom (GCR). FB, FBCR, and GCR IMCT plans were compared for ten pancreas cases. The FBCR plans show comparable PTV coverage and OAR doses for each pancreas case. In conclusion, the dosimetric limitation of fixed beams in heavy ion radiotherapy may be largely mitigated with integrated beam orientation optimization of the couch rotation.
Keywords: beam orientation; carbon ion; gantry; heavy ion; optimization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated beam orientation and scanning-spot optimization in intensity-modulated proton therapy for brain and unilateral head and neck tumors.Med Phys. 2018 Apr;45(4):1338-1350. doi: 10.1002/mp.12788. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29394454 Free PMC article.
-
Toward the combined optimization of dynamic axes (CODA) for stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery using fixed couch trajectories.Med Phys. 2020 Feb;47(2):307-316. doi: 10.1002/mp.13887. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 31659750
-
Pelvic organ motion and dosimetric implications during horizontal patient rotation for prostate radiation therapy.Med Phys. 2021 Jan;48(1):397-413. doi: 10.1002/mp.14579. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33151543
-
A novel energy layer optimization framework for spot-scanning proton arc therapy.Med Phys. 2020 Jun;47(5):2072-2084. doi: 10.1002/mp.14083. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32040214 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in light ion radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Feb 1;58(2):603-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.034. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 14751534 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment Planning Comparison of Gantry-based and Fixed Beams for the Treatment of Liver Tumors With Carbon Ion Therapy.In Vivo. 2024 Nov-Dec;38(6):3002-3010. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13783. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 39477437 Free PMC article.
-
A unified path seeking algorithm for IMRT and IMPT beam orientation optimization.Phys Med Biol. 2023 Sep 22;68(19):10.1088/1361-6560/acf63f. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/acf63f. Phys Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37659406 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical HDR prostate brachytherapy planning with automatic catheter and isotope selection.Med Phys. 2023 Oct;50(10):6525-6534. doi: 10.1002/mp.16677. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 37650773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogata T, Teshima T, Kagawa K, et al. Particle Irradiation Suppresses Metastatic Potential of Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. Published online 2005:9. - PubMed
