Integrated pathway engineering and transcriptome analysis for improved astaxanthin biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica
- PMID: 36092272
- PMCID: PMC9428815
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.08.001
Integrated pathway engineering and transcriptome analysis for improved astaxanthin biosynthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica
Abstract
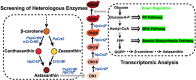
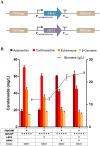
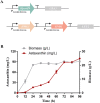
Astaxanthin is a high value carotenoid with a broad range of commercial applications due to its superior antioxidant properties. In this study, β-carotene-producing Yarrowia lipolytica XK17 constructed in the lab was employed for astaxanthin biosynthesis. The catalytic effects of β-carotene ketolase CrtW and β-carotene hydroxylase CrtZ from various species were investigated. The PspCrtW from Paracoccus sp. and HpCrtZ# from Haematococcus pluvialis were confirmed to be the best combination in converting β-carotene. Several key bottlenecks in biomass and astaxanthin biosynthesis were effectively eliminated by optimizing the expression of the above enzymes and restoring uracil/leucine biosynthesis. In addition, the effects of astaxanthin biosynthesis on cell metabolism were investigated by integrated analysis of pathway modification and transcriptome information. After further optimization, strain DN30 was able to synthesize up to 730.3 mg/L astaxanthin in laboratory 5-L fermenter. This study provides a good metabolic strategy and a sustainable development platform for high-value carotenoid production.
Keywords: Astaxanthin; Pathway engineering; Transcriptome analysis; Yarrowia lipolytica.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Production of High Levels of 3S,3'S-Astaxanthin in Yarrowia lipolytica via Iterative Metabolic Engineering.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 Mar 2;70(8):2673-2683. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c08072. Epub 2022 Feb 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35191700
-
Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for production of astaxanthin.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2017 Oct 20;2(4):287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2017.10.002. eCollection 2017 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29552653 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient production of astaxanthin in Yarrowia lipolytica through metabolic and enzyme engineering.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 28;10(3):737-750. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2025.02.014. eCollection 2025 Sep. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40248487 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of microalgal β-carotene and astaxanthin: exploring their health-promoting properties under the effect of salinity and light intensity.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2025 Feb 14;18(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13068-025-02612-x. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2025. PMID: 39953577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of microbial cell factories for astaxanthin production: Biosynthesis and regulations, engineering strategies and fermentation optimization strategies.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 18;7(2):689-704. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.01.002. eCollection 2022 Jun. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35261927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Screening and characterization of integration sites based on CRISPR-Cpf1 in Pichia pastoris.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Jun 18;9(4):759-765. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.06.002. eCollection 2024 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39007090 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering transcriptional regulatory networks for improving second-generation fuel ethanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Oct 28;10(1):207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.10.006. eCollection 2025. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39558946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Customizable and stable multilocus chromosomal integration: a novel glucose-dependent selection system in Aureobasidium spp.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Jun 17;17(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02531-3. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 38886802 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Engineering of Model Microorganisms for the Production of Xanthophyll.Microorganisms. 2023 May 9;11(5):1252. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051252. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jiang G.L., Zhou L.Y., Wang Y.T., Zhu M.J. Astaxanthin from Jerusalem artichoke: production by fed-batch fermentation using Phaffia rhodozyma and application in cosmetics. Process Biochem. 2017;63:16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2017.08.013. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

