Roles of microRNAs in abiotic stress response and characteristics regulation of plant
- PMID: 36092392
- PMCID: PMC9459240
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.919243
Roles of microRNAs in abiotic stress response and characteristics regulation of plant
Abstract
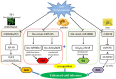
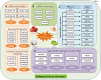
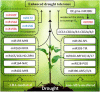
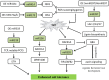
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding endogenous small RNAs (long 20-24 nucleotides) that negatively regulate eukaryotes gene expression at post-transcriptional level via cleavage or/and translational inhibition of targeting mRNA. Based on the diverse roles of miRNA in regulating eukaryotes gene expression, research on the identification of miRNA target genes has been carried out, and a growing body of research has demonstrated that miRNAs act on target genes and are involved in various biological functions of plants. It has an important influence on plant growth and development, morphogenesis, and stress response. Recent case studies indicate that miRNA-mediated regulation pattern may improve agronomic properties and confer abiotic stress resistance of plants, so as to ensure sustainable agricultural production. In this regard, we focus on the recent updates on miRNAs and their targets involved in responding to abiotic stress including low temperature, high temperature, drought, soil salinity, and heavy metals, as well as plant-growing development. In particular, this review highlights the diverse functions of miRNAs on achieving the desirable agronomic traits in important crops. Herein, the main research strategies of miRNAs involved in abiotic stress resistance and crop traits improvement were summarized. Furthermore, the miRNA-related challenges and future perspectives of plants have been discussed. miRNA-based research lays the foundation for exploring miRNA regulatory mechanism, which aims to provide insights into a potential form of crop improvement and stress resistance breeding.
Keywords: abiotic stress; agronomic trait; growing development; microRNA; target gene.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Yang, Zhang, Wu and Si.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation mechanism of microRNA in plant response to abiotic stress and breeding.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):1447-1457. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4511-2. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30465132 Review.
-
Functional Roles of microRNAs in Agronomically Important Plants-Potential as Targets for Crop Improvement and Protection.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Mar 22;8:378. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00378. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28382044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs As Potential Targets for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Jun 14;7:817. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00817. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27379117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional role of microRNA in the regulation of biotic and abiotic stress in agronomic plants.Front Genet. 2023 Oct 10;14:1272446. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1272446. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37886688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses in crop plants.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Sep;174(1):93-115. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-0914-2. Epub 2014 May 29. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24869742 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of microRNAs That Provide a Low Light Stress Tolerance-Mediated Signaling Pathway during Vegetative Growth in Rice.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;11(19):2558. doi: 10.3390/plants11192558. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36235424 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulators of Plant Adaptation to Heat Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 27;24(17):13297. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713297. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Plant Epigenetic Regulation in Response to Plant Stress: Recent Discoveries and Implications.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 7;13(2):163. doi: 10.3390/plants13020163. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant miR8126-3p and miR8126-5p Decrease Lipid Accumulation through Modulation of Metabolic Genes in a Human Hepatocyte Model That Mimics Steatosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 31;25(3):1721. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031721. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338999 Free PMC article.
-
ASmiR: a machine learning framework for prediction of abiotic stress-specific miRNAs in plants.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Mar 20;23(2):92. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01014-2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36939943
References
-
- Anjali N., Nadiya F., Thomas J., Sabu K. K. (2018). Identification and characterization of drought responsive microRNAs and their target genes in cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum Maton). Plant Growth Regul. 87, 201–216. 10.1007/s10725-018-0462-9 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

