Antigen presentation by cardiac fibroblasts promotes cardiac dysfunction
- PMID: 36092510
- PMCID: PMC9451034
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-022-00116-7
Antigen presentation by cardiac fibroblasts promotes cardiac dysfunction
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Antigen presentation by cardiac fibroblasts promotes cardiac dysfunction.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Dec;1(12):1230. doi: 10.1038/s44161-022-00179-6. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 39196170 No abstract available.
Abstract
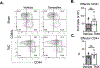
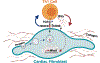
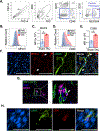
Heart failure (HF) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Studies in animal models and patients with HF revealed a prominent role for CD4+ T cell immune responses in the pathogenesis of HF and highlighted an active crosstalk between cardiac fibroblasts and IFNγ producing CD4+ T cells that results in profibrotic myofibroblast transformation. Whether cardiac fibroblasts concomitantly modulate pathogenic cardiac CD4+ T cell immune responses is unknown. Here we show report that murine cardiac fibroblasts express major histocompatibility complex type II (MHCII) in two different experimental models of cardiac inflammation. We demonstrate that cardiac fibroblasts take up and process antigens for presentation to CD4+ T cells via MHCII induced by IFNγ. Conditional deletion of MhcII in cardiac fibroblasts ameliorates cardiac remodelling and dysfunction induced by cardiac pressure overload. Collectively, we demonstrate that cardiac fibroblasts function as antigen presenting cells (APCs) and contribute to cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction through IFNγ induced MHCII.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
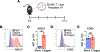









References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
