A Rearrangement Reaction to Yield a NH4 + Ion Driven by Polyoxometalate Formation
- PMID: 36092612
- PMCID: PMC9454273
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04015
A Rearrangement Reaction to Yield a NH4 + Ion Driven by Polyoxometalate Formation
Abstract
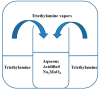
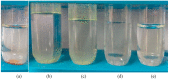
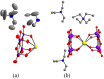
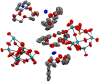
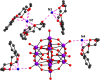
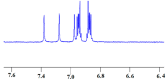
Triethylamine is a volatile liquid and exists in the atmosphere in the gas phase. It is a hazardous air pollutant and identified as a toxic air contaminant. Thus, producing ammonia (a vital chemical for fertilizer production) from the vapor state of this toxic substance is a challenging task. Diffusion of the vapor of triethylamine, (C2H5)3N, into an acidified aqueous solution of sodium molybdate results in the formation of single crystals of compound [(C2H5)3NH]2[(C2H5)4N][NaMo8O26] (1). Notably, compound 1 includes a [(C2H5)4N]+ cation, even though the concerned reaction mixture was not treated with any tetraethylammonium salt. The formation of the [(C2H5)4N]+ cation from (C2H5)3N in an acidic aqueous medium is logically possible only when an ammonium cation (NH4 +) is formed in the overall reaction: 4(C2H5)3N + 4H+ = 3[(C2H5)4N]+ + [NH4]+. Although the resulting NH4 + cation (identified by Nessler's reagent test) is not included in the crystals of compound 1 as a cation, it can be made associated with a crown ether in the isolation of single crystals of compound [NH4⊂B15C5]3[PMo12O40]·B15C5 (2), (B15C5 = benzo-15-crown-5). Crystal structure analysis and 1H NMR studies of compound 2 have established the presence of an H-bonded NH4 + ion in compound 2, thereby established the rearrangement reaction.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Organic-inorganic interactions revealed by Raman spectroscopy during reversible phase transitions in semiconducting [(C2H5)4N]FeCl4.RSC Adv. 2021 May 24;11(30):18651-18660. doi: 10.1039/d1ra02475b. eCollection 2021 May 19. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35480942 Free PMC article.
-
Supramolecular cation assemblies of hydrogen-bonded (NH4+/NH2NH3+)(crown ether) in [Ni(dmit)2]-based molecular conductors and magnets.J Am Chem Soc. 2002 Jul 31;124(30):8903-11. doi: 10.1021/ja026211g. J Am Chem Soc. 2002. PMID: 12137545
-
The effect of counteranions on the molecular structures of phosphanegold(i) cluster cations formed by polyoxometalate (POM)-mediated clusterization.Dalton Trans. 2016 Sep 14;45(34):13565-75. doi: 10.1039/c6dt02670b. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Dalton Trans. 2016. PMID: 27511307
-
A Series of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Compounds [(C2H5)4N]InCl4-xBrx (x = 0, 2, 4): Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Nonlinear Optical Properties.Inorg Chem. 2020 Apr 20;59(8):5721-5727. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00508. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Inorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32233404
-
Proof of ion-pair structures in ammonium-based protic ionic liquids using combined NMR and DFT/PCM-based chemical shift calculations.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017 Sep 20;19(36):25033-25043. doi: 10.1039/c7cp04481j. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 28876338
Cited by
-
Isolation and characterization of cadmium-resistant Bacillus cereus strains from Cd-contaminated mining areas for potential bioremediation applications.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 12;16:1550830. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1550830. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40012780 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

