Microarray and Bioinformatics Analysis of Differential Gene and lncRNA Expression during Erythropoietin Treatment of Acute Spinal Cord Injury in Rats
- PMID: 36092786
- PMCID: PMC9462987
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4121910
Microarray and Bioinformatics Analysis of Differential Gene and lncRNA Expression during Erythropoietin Treatment of Acute Spinal Cord Injury in Rats
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Microarray and Bioinformatics Analysis of Differential Gene and lncRNA Expression during Erythropoietin Treatment of Acute Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9843413. doi: 10.1155/2023/9843413. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 38094373 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Purpose: We performed a genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) expression to identify novel targets for the further study of recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) treatment of acute spinal cord injury (SCI) in rats.
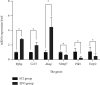
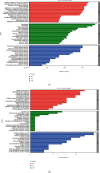
Methods: Nine rats were randomly divided into 3 groups. No operation was performed in group 1. In groups 2 and 3, a laminectomy was performed at the 10th thoracic vertebra, and a contusion injury was induced by extradural application of an aneurysm clip. Group 1 rats did not receive any treatment, group 2 rats received a single intraperitoneal injection of normal saline, and group 3 rats received rhEPO. Three days after injury, spinal cord tissues were collected for RNA-Seq, microarray, differentially expressed genes (DEGs), Gene Ontology (GO) function enrichment, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment, and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analyses.
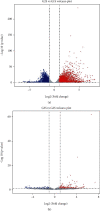
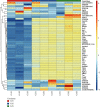
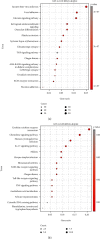
Results: Compared with group 1, 4,446 genes were found to be differentially expressed in group 2. Furthermore, 99 lncRNAs were found to be changed in the injury group. The data indicate that 2,471 mRNAs were upregulated, and 1,975 mRNAs were downregulated in group 2 as compared with group 1. In addition, 45 of the lncRNAs were upregulated, and the other 44 lncRNAs were downregulated. The top 5 upregulated and top 5 downregulated lncRNAs that were different between group 2 and group 1 are shown. The top 5 downregulated and the top 5 upregulated lncRNAs that were different between group 3 and group 2 are shown.
Conclusion: RhEPO treatment alters the expression profiles of the differentially expressed lncRNAs and genes beneficial to the development of new treatments.
Copyright © 2022 Haibo He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation of candidate long noncoding RNAs and messenger RNAs in the immediate phase of spinal cord injury based on gene expression profiles.Gene. 2018 Jun 30;661:119-125. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.074. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29580899
-
Signatures of altered long noncoding RNAs and messenger RNAs expression in the early acute phase of spinal cord injury.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8918-8927. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27560. Epub 2018 Oct 20. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30341912
-
Analyses of long non-coding RNA and mRNA profiles in the spinal cord of rats using RNA sequencing during the progression of neuropathic pain in an SNI model.RNA Biol. 2017 Dec 2;14(12):1810-1826. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1371400. Epub 2017 Sep 29. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28854101 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment in Spinal Cord Injury Recovery: Profiling Long Noncoding RNAs.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2023 Feb 1;48(3):213-222. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004525. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2023. PMID: 36607628
-
Research Progress of Long Non-coding RNAs in Spinal Cord Injury.Neurochem Res. 2023 Jan;48(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03720-y. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 35974214 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Microarray and Bioinformatics Analysis of Differential Gene and lncRNA Expression during Erythropoietin Treatment of Acute Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9843413. doi: 10.1155/2023/9843413. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 38094373 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

