LncRNA RP11-59J16.2 aggravates apoptosis and increases tau phosphorylation by targeting MCM2 in AD
- PMID: 36092938
- PMCID: PMC9459667
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.824495
LncRNA RP11-59J16.2 aggravates apoptosis and increases tau phosphorylation by targeting MCM2 in AD
Abstract
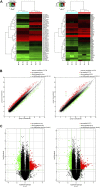
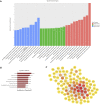
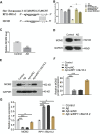
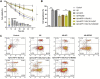
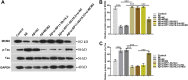
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a degenerative disease of central nervous system with unclear pathogenesis, accounting for 60%-70% of dementia cases. Long noncoding RNAs (LncRNAs) play an important function in the development of AD. This study aims to explore the role of differentially expressed lncRNAs in AD patients' serum in the pathogenesis of AD. Microarray analysis was performed in the serum of AD patients and healthy controls to establish lncRNAs and mRNAs expression profiles. GO analysis and KEGG pathway analysis revealed that G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle might be involved in the development of AD. The result showed that RP11-59J16.2 was up-regulated and MCM2 was down-regulated in serum of AD patients. SH-SY5Y cells were treated with Aβ 1-42 to establish AD cell model. Dual luciferase reporter gene analysis verified that RP11-59J16.2 could directly interact with 3'UTR of MCM2 and further regulate the expression of MCM2. Inhibition of RP11-59J16.2 or overexpression of MCM2, CCK-8 assay and Annexin V FITC/PI apoptosis assay kit results showed that RP11-59J16.2 could reduce cell viability, aggravate apoptosis and increase Tau phosphorylation in AD cell model by inhibiting MCM2. In short, our study revealed a novel lncRNA RP11-59J16.2 that could promote neuronal apoptosis and increase Tau phosphorylation by regulating MCM2 in AD model, and indicated that lncRNA RP11-59J16.2 might be a potential target molecule for AD development.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; MCM2; P-tau; RP11-59J16.2; apoptosis; microarray analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Guan, Gao, Dai, Li, Bao and Gu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
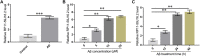
Similar articles
-
Differentially expressed long-chain noncoding RNAs in human neuroblastoma cell line (SH-SY5Y): Alzheimer's disease cell model.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2019;82(19):1052-1060. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2019.1687183. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2019. PMID: 31722651
-
Knockdown of Long Non-Coding RNA RP11-445H22.4 Alleviates LPS-Induced Injuries by Regulation of MiR-301a in Osteoarthritis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(2):832-843. doi: 10.1159/000487175. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29414810
-
Super-enhancer-associated long noncoding RNA RP11-569A11.1 inhibited cell progression and metastasis by regulating IFIT2 in colorectal cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jun;35(6):e23780. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23780. Epub 2021 May 4. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33942366 Free PMC article.
-
The binding of lncRNA RP11-732M18.3 with 14-3-3 β/α accelerates p21 degradation and promotes glioma growth.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jul;45:58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 13. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31202814 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA NEAT1 promotes Alzheimer's disease by down regulating micro-27a-3p.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):8885-8896. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34540002 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
KNTC1 and MCM2 are the molecular targets of gallbladder cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Jul 21;15(14):7008-7022. doi: 10.18632/aging.204889. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37480569 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic identification and experiment validation reveal 6 hub genes, promising diagnostic and therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's disease.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jan 2;17(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01775-6. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38167011 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs: Crucial Regulators in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis and Prospects for Precision Medicine.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jun;62(6):7525-7541. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04729-4. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39907902 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs involved in the molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jun 28;18:1421675. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1421675. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39005845 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Inhibits Cell Cycle Progression and Cell Proliferation in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells via the miR-212-3p/MCM2 Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 1;24(3):2788. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032788. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker W. W., Luis C. A., Kashuba A., Luis M., Harwood D. G., Loewenstein D., et al. (2002). Relative frequencies of alzheimer disease, lewy body, vascular and frontotemporal dementia, and hippocampal sclerosis in the state of florida Brain Bank. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 16 (4), 203–212. 10.1097/00002093-200210000-00001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

