Development and Validation of a Multivariable Prediction Model to Identify Acute Exacerbation of COPD and Its Severity for COPD Management in China (DETECT Study): A Multicenter, Observational, Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 36092968
- PMCID: PMC9462440
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S363935
Development and Validation of a Multivariable Prediction Model to Identify Acute Exacerbation of COPD and Its Severity for COPD Management in China (DETECT Study): A Multicenter, Observational, Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Purpose: There is an unmet clinical need for an accurate and objective diagnostic tool for early detection of acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD). DETECT (NCT03556475) was a multicenter, observational, cross-sectional study aiming to develop and validate multivariable prediction models for AECOPD occurrence and severity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in China.
Patients and methods: Patients aged ≥40 years with moderate/severe COPD, AECOPD, or no COPD were consecutively enrolled between April 22, 2020, and January 18, 2021, across seven study sites in China. Multivariable prediction models were constructed to identify AECOPD occurrence (primary outcome) and AECOPD severity (secondary outcome). Candidate variables were selected using a stepwise procedure, and the bootstrap method was used for internal model validation.
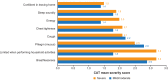
Results: Among 299 patients enrolled, 246 were included in the final analysis, of whom 30.1%, 40.7%, and 29.3% had COPD, AECOPD, or no COPD, respectively. Mean age was 64.1 years. Variables significantly associated with AECOPD occurrence (P<0.05) and severity (P<0.05) in the final models included COPD disease-related characteristics, as well as signs and symptoms. Based on cut-off values of 0.374 and 0.405 for primary and secondary models, respectively, the performance of the primary model constructed to identify AECOPD occurrence (AUC: 0.86; sensitivity: 0.84; specificity: 0.77), and of the secondary model for AECOPD severity (AUC: 0.81; sensitivity: 0.90; specificity: 0.73) indicated high diagnostic accuracy and clinical applicability.
Conclusion: By leveraging easy-to-collect patient and disease data, we developed identification tools that can be used for timely detection of AECOPD and its severity. These tools may help physicians diagnose AECOPD in a timely manner, before further disease progression and possible hospitalizations.
Keywords: acute exacerbation; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; diagnosis; prediction model.
© 2022 Yin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Multiple Factor Analysis of Depression and/or Anxiety in Patients with Acute Exacerbation Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020 Jun 19;15:1449-1464. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S245842. eCollection 2020. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020. PMID: 32606653 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Acute COPD Exacerbation in the Swiss Multicenter COPD Cohort Study (TOPDOCS) by Clinical Parameters, Medication Use, and Immunological Biomarkers.Respiration. 2022;101(5):441-454. doi: 10.1159/000520196. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Respiration. 2022. PMID: 34942619 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbation in patients with stable COPD in China: analysis of a prospective, 52-week, nationwide, observational cohort study (REAL).Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2023 Jan-Dec;17:17534666231167353. doi: 10.1177/17534666231167353. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2023. PMID: 37073797 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics, Management and In-Hospital Clinical Outcomes Among Inpatients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in China: Results from the Phase I Data of ACURE Study.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Feb 25;16:451-465. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S281957. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 33658775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expert consensus on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the People's Republic of China.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014 Apr 25;9:381-95. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S58454. eCollection 2014. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014. PMID: 24812503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Diagnostic Systems for COPD Exacerbation in the Older People: Present and Future].Open Respir Arch. 2023 Dec 1;6(1):100291. doi: 10.1016/j.opresp.2023.100291. eCollection 2024 Jan-Mar. Open Respir Arch. 2023. PMID: 38187887 Free PMC article. Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Treatment patterns in patients with stable COPD in China: analysis of a prospective, 52-week, nationwide, observational cohort study (REAL).Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2023 Jan-Dec;17:17534666231158283. doi: 10.1177/17534666231158283. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2023. PMID: 37013442 Free PMC article.
-
Treatable traits identified in Chinese patients hospitalized with AECOPD: A Multicenter Cohort Study.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Apr 13;22(9):2227-2236. doi: 10.7150/ijms.111294. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40303489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2022 report); 2022. Available from: https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/GOLD-REPORT-2022-v1.1-22.... Accessed February 14, 2022.
-
- Guo J, Chen Y, Zhang W, Tong S, Dong J. Moderate and severe exacerbations have a significant impact on health-related quality of life, utility, and lung function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2020;78:28–35. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.04.010 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

