Multiplexed protein profiling reveals spatial subcellular signaling networks
- PMID: 36093051
- PMCID: PMC9460555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104980
Multiplexed protein profiling reveals spatial subcellular signaling networks
Abstract
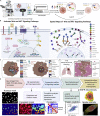
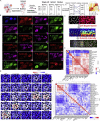
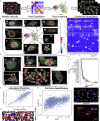
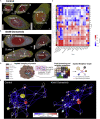
Protein-protein interaction networks are altered in multi-gene dysregulations in many disorders. Image-based protein multiplexing sheds light on signaling pathways to dissect cell-to-cell heterogeneity, previously masked by the bulk assays. Herein, we present a rapid multiplexed immunofluorescence (RapMIF) method measuring up to 25-plex spatial protein maps from cultures and tissues at subcellular resolution, providing combinatorial 272 pairwise and 1,360 tri-protein signaling states across 33 multiplexed pixel-level clusters. The RapMIF pipeline automated staining, bleaching, and imaging of the biospecimens in a single platform. RapMIF showed that WNT/β-catenin signaling upregulated upon the inhibition of the AKT/mTOR pathway. Subcellular protein images demonstrated translocation patterns, spatial receptor discontinuity, and subcellular signaling clusters in single cells. Signaling networks exhibited spatial redistribution of signaling proteins in drug-responsive cultures. Machine learning analysis predicted the phosphorylated β-catenin expression from interconnected signaling protein images. RapMIF is an ideal signaling discovery approach for precision therapy design.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Biological sciences research methodologies; Biology experimental methods; Biotechnology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

