E2F1 as a potential prognostic and therapeutic biomarker by affecting tumor development and immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36093522
- PMCID: PMC9459514
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-218
E2F1 as a potential prognostic and therapeutic biomarker by affecting tumor development and immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: E2F1 plays a crucial role in cell cycle regulation. However, the exact role of E2F1 in liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC) remains controversial. This study aimed to integrate disparate data by bioinformatics for a deeper insight into the possible roles of E2F1 in LIHC.
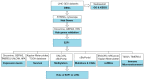
Methods: Differentially overexpressed genes in LIHC were screened by GEO2R. Gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway were analyzed by WebGestalt. Then, hub genes were selected via STRING and Cytoscape, followed by validation with Oncomine, GEPIA2, and Human Protein Atlas (HPA). Next, E2F1 expression was investigated using Oncomine, GEPIA2, TIMER2.0, UALCAN, and HPA. Then, Kaplan-Meier plotter was adopted to investigate survival. After that, E2F1 promotor methylation, mutations and copy number alterations were analyzed with UALCAN and cBioPortal. Moreover, competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) network were established using ENCORI, miRCancer, and Kaplan-Meier plotter. Additionally, the association between E2F1 and immune microenvironment was investigated through TISCH and TIMER2.0.
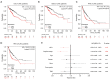
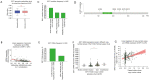
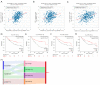
Results: Six hub genes including E2F1 were identified. E2F1 was overexpressed in most solid cancers including LIHC. E2F1 overexpression was correlated with poor prognosis in LIHC. Copy number alterations could positively affect E2F1 expression. Moreover, ceRNAs network was established with 3 long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) named AC025048.4, AC090114.2, and AC092171.5, as well as 4 microRNAs (miRNAs) including miR-150-5p, miR-302c-3p, miR-520d-3p, and miR-330-5p. Single cell sequencing data showed that E2F1 was mainly expressed in malignant cells and proliferating T cells, and that E2F targets almost exclusively enriched in proliferating T cells. Besides, there existed a positive correlation between E2F1 and certain immune cells including CD8(+) T cells, CD4(+) T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
Conclusions: This study elucidated that E2F1 could affect tumor development and immune microenvironment in LIHC. Thus, E2F1 might be a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for LIHC.
Keywords: E2F1; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis; therapeutic target; tumor microenvironment.
2022 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-22-218/coif). ZT reports grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2018A030313530); the Chinese Scholarship Council (No. 201908440010); the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission Project (No. JCYJ20210324110408022); and the Beijing Bethune Charitable Foundation (No. flzh202120). YL reports grants from the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission Project (Nos. GJHZ20180420180754917, ZDSYS20190902092855097, KCXFZ20200201101050887 and GJHZ20200731095207023); and the Shenzhen Sanming Project (No. SZSM201612041). The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
