Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1) in gastric cancer
- PMID: 36093558
- PMCID: PMC9459500
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-303
Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1) in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1) is a member of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) family and has recently been reported to contribute to development and progression of various tumors. However, the clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of PTBP1 in gastric cancer have not been sufficiently elucidated.
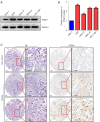
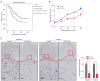
Methods: Bioinformatic analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data were employed to analyze the expression of PTBP1 mRNA and its prognostic value in gastric cancer. The expression type of PTBP1 in gastric cancer cells was further confirmed through reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blot assay. Then, the association between PTBP1 protein expression and clinicopathological features was analyzed based on immunohistochemical staining results in gastric cancer tissue microarray including 311 cases. The prognostic value of PTBP1 protein was explored through univariate and multivariate analyses. Additionally, cell count and transwell assay were performed to detect the biological role of PTBP1 in gastric cancer cells in vitro.
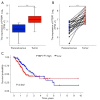
Results: PTBP1 was highly expressed in gastric cancer cells and tissues at mRNA and protein level. High expression of PTBP1 was closely related to several clinicopathological features, including gender, age at surgery, histological type, TNM stage and lymph node metastasis. Moreover, high expression PTBP1 predicts poor prognosis, and may be an independent prognostic factor for overall survival in gastric cancer patients. Knockdown of PTBP1 substantially suppressed the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells in vitro.
Conclusions: PTBP1 is up-regulated and predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer. PTBP1 may serve as a biomarker of poor prognosis and a novel target in treating gastric cancer.
Keywords: Polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1); gastric cancer (GC); immunohistochemistry; migration; prognosis.
2022 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-22-303/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune-Related miRNA-195-5p Inhibits the Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Targeting Polypyrimidine Tract-Binding Protein 1.Front Oncol. 2022 May 5;12:862564. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.862564. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35600383 Free PMC article.
-
PTBP1 knockdown in renal cell carcinoma inhibits cell migration, invasion and angiogenesis in vitro and metastasis in vivo via the hypoxia inducible factor-1α pathway.Int J Oncol. 2018 May;52(5):1613-1622. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4296. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29512730
-
PTBP1 is a Novel Poor Prognostic Factor for Glioma.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Mar 8;2022:7590997. doi: 10.1155/2022/7590997. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35299889 Free PMC article.
-
PTBP1 plays an important role in the development of gastric cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Sep 5;23(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03043-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37670313 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of PTBP1 in alternative splicing, glycolysis, and oncogensis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Feb.;21(2):122-136. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1900422. Epub 2020 Feb 5. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 32115910 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PTBP1 as a potential regulator of disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Nov;479(11):2875-2894. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04905-x. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38129625 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
