Diagnosis and prognostic analysis of skin infiltration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 36093559
- PMCID: PMC9459570
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-21-2864
Diagnosis and prognostic analysis of skin infiltration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a malignant lymphoproliferative disorder; excessive aggregation of small mature B cells in peripheral blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen is characteristic. Cutaneous involvement of CLL can be classified into specific skin lesions, including skin infiltration by leukemic cells, secondary cutis tumors, nonspecific lesions and associated skin diseases. Uncommonly, skin infiltration in patients who are diagnosed with CLL can be localized or widespread, and it can take various forms, including nodules, plaques, papules, and ulcers.
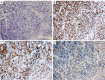
Case description: We report a 52-year-old patient diagnosed for CLL with skin infiltration, whose lesions were subcutaneous nodules, widely distributed in the nasal base, right auricle, extremities, and trunk. Lesions are firm, without tenderness and have poor mobility. Spontaneous regression of some skin lesions is the most prominent feature. The pathological biopsy of skin tissue showed that small round cells infiltrated subcutaneous adipose tissue. The immunohistochemical results were consistent with the immunophenotype of neoplastic B cells, and the aberrant co-expression of CD5 and CD23 was the significant marker. The patient is currently being followed up.
Conclusions: Aggressive treatment of the primary disease can alleviate the skin symptoms to a certain extent, and the prognosis of patients is affected by multiple factors such as the extent of the lesions, whether accompanied by epidermal changes, the site of infiltration and the percentage of small B lymphocytes. Long-term follow-up is necessary.
Keywords: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); case report; diagnosis; prognosis; skin infiltration.
2022 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-21-2864/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cutaneous manifestations of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Int J Hematol. 2020 Oct;112(4):459-465. doi: 10.1007/s12185-020-02978-8. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Int J Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32889697 Review.
-
[Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia presenting with specific cutaneous infiltrates in the absence of lymphocytosis: Two cases].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2012 Oct;139(10):641-6. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2012.06.040. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2012. PMID: 23122378 French.
-
Leukemia cutis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia presenting as an episodic papulovesicular eruption.Dermatol Online J. 2011 Sep 15;17(9):7. Dermatol Online J. 2011. PMID: 21971272
-
Specific cutaneous infiltrates of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia arising at the site of herpes zoster and herpes simplex scars.Cancer. 1995 Jul 1;76(1):26-31. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950701)76:1<26::aid-cncr2820760105>3.0.co;2-j. Cancer. 1995. PMID: 8630873
-
Skin lesions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2007 May;48(5):855-65. doi: 10.1080/10428190601137336. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007. PMID: 17487727 Review.
Cited by
-
Oh node: Extranodal nodular involvement of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the colon.Am J Hematol. 2025 Feb;100(2):298-299. doi: 10.1002/ajh.27467. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Am J Hematol. 2025. PMID: 39194301 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dhir R. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia manifestating as exfoliative dermatitis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 1995;61:102-3. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
