Construction of miRNA-mRNA network and a nomogram model of prognostic analysis for prostate cancer
- PMID: 36093560
- PMCID: PMC9459648
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-22-653
Construction of miRNA-mRNA network and a nomogram model of prognostic analysis for prostate cancer
Abstract
Background: Dysregulated genetic factors correlate with carcinoma progression. However, the hub miRNAs-mRNAs related to biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer remain unclear. We aim to identify potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory network and hub genes in prostate cancer.
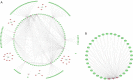
Methods: Datasets of gene expression microarray were downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database for Robust Rank Aggregation (RRA), targeted gene prediction, gene function and signal pathway enrichment analyses, miRNA-mRNA regulatory network construction, core network screening, as well as validation and survival analysis were carried out by using exogenous data.
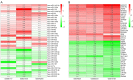
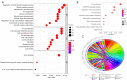
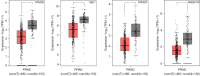
Results: Prostate cancer-related differentially expressed genes were mostly related to actin filament regulation. Moreover, the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway might play a role in prostate cancer progression. As the core of microRNAs, hsa-miR-106b-5p, hsa-miR-17-5p and hsa-miR-183-5p were matched to hub genes (such as TMEM100, FRMD6, NBL1 and STARD4). The expression levels of hub genes in prostate cancer tissues were significantly lower than normal and closely related to prognosis of patients. The ridge regression model was applied to establish a risk score system. Both risk score and Gleason were used to establish a nomogram. Nomogram predicted the area under the [receiver operating characteristic (ROC)] curve (AUC) of biochemical recurrence at 1-, 3-, and 5-year of 0.713, 0.732 and 0.753, respectively.
Conclusions: Hub genes were closely related to prostate cancer development and progression, which might become biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis. This novel nomogram established could be applied to clinical prediction.
Keywords: Prostate cancer; bioinformatics; microRNA-mRNA (miRNA-mRNA); nomogram; prognosis.
2022 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-22-653/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using biological information to analyze potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in the plasma of patients with non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 21;22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09281-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35313857 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating microRNA expression, miRNA-mRNA regulation network and signal pathway: a novel strategy for lung cancer biomarker discovery.PeerJ. 2021 Oct 25;9:e12369. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12369. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34754623 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray data analysis on gene and miRNA expression to identify biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Apr 16;20(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06829-x. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32299382 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of mRNA-single nucleotide polymorphism-microRNA interaction network to identify biomarkers associated with prostate cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 25;13:922712. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.922712. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35957689 Free PMC article.
-
GNL3 and PA2G4 as Prognostic Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 11;15(10):2723. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102723. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345060 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel tumor purity and immune infiltration-related model for predicting distant metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Nov 28;28(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01522-8. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38017548 Free PMC article.
-
Development and external validation of a nomogram to predict the prognosis of patients with metastatic prostate cancer who underwent radiotherapy.Gland Surg. 2024 Nov 30;13(11):2137-2147. doi: 10.21037/gs-24-313. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Gland Surg. 2024. PMID: 39678407 Free PMC article.
-
A panel based on three-miRNAs as diagnostic biomarker for prostate cancer.Front Genet. 2024 May 16;15:1371441. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1371441. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38818039 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of the potential roles of microRNA-messenger RNA networks in prostate adenocarcinoma.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 17;9(12):e22383. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22383. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38076048 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
