Architectures and complex functions of tandem riboswitches
- PMID: 36093908
- PMCID: PMC9481103
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2119017
Architectures and complex functions of tandem riboswitches
Abstract
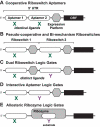
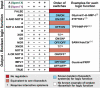
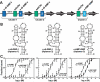
Riboswitch architectures that involve the binding of a single ligand to a single RNA aptamer domain result in ordinary dose-response curves that require approximately a 100-fold change in ligand concentration to cover nearly the full dynamic range for gene regulation. However, by using multiple riboswitches or aptamer domains in tandem, these ligand-sensing structures can produce additional, complex gene control outcomes. In the current study, we have computationally searched for tandem riboswitch architectures in bacteria to provide a more complete understanding of the diverse biological and biochemical functions of gene control elements that are made exclusively of RNA. Numerous different arrangements of tandem homologous riboswitch architectures are exploited by bacteria to create more 'digital' gene control devices, which operate over a narrower ligand concentration range. Also, two heterologous riboswitch aptamers are sometimes employed to create two-input Boolean logic gates with various types of genetic outputs. These findings illustrate the sophisticated genetic decisions that can be made by using molecular sensors and switches based only on RNA.
Keywords: Aptamer; gene regulation; logic gate; noncoding RNA; transcription control; translation control.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tandem riboswitches form a natural Boolean logic gate to control purine metabolism in bacteria.Elife. 2018 Mar 5;7:e33908. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33908. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29504937 Free PMC article.
-
The asymmetry and cooperativity of tandem glycine riboswitch aptamers.RNA. 2020 May;26(5):564-580. doi: 10.1261/rna.073577.119. Epub 2020 Jan 28. RNA. 2020. PMID: 31992591 Free PMC article.
-
Tandem riboswitch architectures exhibit complex gene control functions.Science. 2006 Oct 13;314(5797):300-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1130716. Science. 2006. PMID: 17038623
-
Riboswitch Mechanisms for Regulation of P1 Helix Stability.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 4;25(19):10682. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910682. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Methods for Modeling Aptamers and Designing Riboswitches.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 17;18(11):2442. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112442. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29149090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and function analysis of a type III preQ1-I riboswitch from Escherichia coli reveals direct metabolite sensing by the Shine-Dalgarno sequence.J Biol Chem. 2023 Oct;299(10):105208. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105208. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37660906 Free PMC article.
-
Co-transcriptional folding orchestrates sequential multi-effector sensing by a glycine tandem riboswitch.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 30:2025.05.28.656632. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656632. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501894 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Harnessing DNA computing and nanopore decoding for practical applications: from informatics to microRNA-targeting diagnostics.Chem Soc Rev. 2025 Jan 2;54(1):8-32. doi: 10.1039/d3cs00396e. Chem Soc Rev. 2025. PMID: 39471098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antisense-acting riboswitches: A poorly characterized yet important model of transcriptional regulation in prokaryotic organisms.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 21;18(2):e0281744. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281744. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36809273 Free PMC article.
-
Customizing cellular signal processing by synthetic multi-level regulatory circuits.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 18;14(1):8415. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44256-1. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38110405 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nahvi A, Sudarsan N, Ebert MS, et al. Genetic control by a metabolite binding mRNA. Chem Biol. 2002;9:1043–1049. - PubMed
-
- Winkler W, Nahvi A, Breaker RR.. Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature. 2002;419:952–956. - PubMed
-
- Mironov AS, Gusarov I, Rafikov R, et al. Sensing small molecules by nascent RNA: a mechanism to control transcription in bacteria. Cell. 2002;111:747–756. - PubMed
-
- Sherwood AV, Henkin TM. Riboswitch-mediated gene regulation: novel RNA architectures dictate gene expression responses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016;70:361–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
