Real-time shimming with FID navigators
- PMID: 36093989
- PMCID: PMC9529812
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29421
Real-time shimming with FID navigators
Abstract
Purpose: To implement a method for real-time field control using rapid FID navigator (FIDnav) measurements and evaluate the efficacy of the proposed approach for mitigating dynamic field perturbations and improving -weighted image quality.
Methods: FIDnavs were embedded in a gradient echo sequence and a subject-specific linear calibration model was generated on the scanner to facilitate rapid shim updates in response to measured FIDnav signals. To confirm the accuracy of FID-navigated field updates, phantom and volunteer scans were performed with online updates of the scanner B0 shim settings. To evaluate improvement in -weighted image quality with real-time shimming, 10 volunteers were scanned at 3T while performing deep-breathing and nose-touching tasks designed to modulate the B0 field. Quantitative image quality metrics were compared with and without FID-navigated field control. An additional volunteer was scanned at 7T to evaluate performance at ultra-high field.
Results: Applying measured FIDnav shim updates successfully compensated for applied global and linear field offsets in phantoms and across all volunteers. FID-navigated real-time shimming led to a substantial reduction in field fluctuations and a consequent improvement in -weighted image quality in volunteers performing deep-breathing and nose-touching tasks, with 7.57% ± 6.01% and 8.21% ± 10.90% improvement in peak SNR and structural similarity, respectively.
Conclusion: FIDnavs facilitate rapid measurement and application of field coefficients for slice-wise B0 shimming. The proposed approach can successfully counteract spatiotemporal field perturbations and substantially improves -weighted image quality, which is important for a variety of clinical and research applications, particularly at ultra-high field.
Keywords: -weighted imaging; B0 inhomogeneity; FID navigators; artifact correction; real-time shimming.
© 2022 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


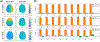
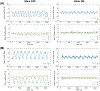
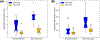
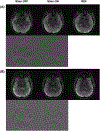
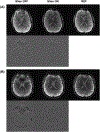
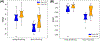

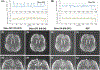
Similar articles
-
Advancements in MR hardware systems and magnetic field control: B0 shimming, RF coils, and gradient techniques for enhancing magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy.Psychoradiology. 2024 Aug 14;4:kkae013. doi: 10.1093/psyrad/kkae013. eCollection 2024. Psychoradiology. 2024. PMID: 39258223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid measurement and correction of spatiotemporal B0 field changes using FID navigators and a multi-channel reference image.Magn Reson Med. 2020 Feb;83(2):575-589. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27957. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Magn Reson Med. 2020. PMID: 31463976 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic distortion correction for functional MRI using FID navigators.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Mar;85(3):1294-1307. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28505. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 32970869 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic B0 shimming at 7 T.Magn Reson Imaging. 2011 May;29(4):483-96. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Mar 12. Magn Reson Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21398062 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo B0 field shimming methods for MRI at 7T.Neuroimage. 2018 Mar;168:71-87. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.06.013. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28602943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid prospective motion correction using free induction decay and stationary field probe navigators at 7T.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Jul;94(1):105-118. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30441. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 39846141 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in MR hardware systems and magnetic field control: B0 shimming, RF coils, and gradient techniques for enhancing magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy.Psychoradiology. 2024 Aug 14;4:kkae013. doi: 10.1093/psyrad/kkae013. eCollection 2024. Psychoradiology. 2024. PMID: 39258223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospective motion correction for and susceptibility mapping using spherical navigators.Magn Reson Med. 2025 Apr;93(4):1642-1656. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30385. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Magn Reson Med. 2025. PMID: 39627965 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van de Moortele P-F, Pfeuffer J, Glover GH, Ugurbil K, Hu X. Respiration-induced B0 fluctuations and their spatial distribution in the human brain at 7 tesla. Magn. Reson. Med 2002;47:888–895. - PubMed
-
- Versluis MJ, Peeters JM, Rooden S Van, Grond J Van Der, Buchem MA Van, Webb AG, Osch MJP Van. Origin and reduction of motion and f0 artifacts in high resolution T2* magnetic resonance imaging: Application in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neuroimage 2010;51:1082–1088. - PubMed
-
- Van Gelderen P, De Zwart JA, Starewicz P, Hinks RS, Duyn JH. Real-time shimming to compensate for respiration-induced B0 fluctuations. Magn. Reson. Med 2007;57:362–368. - PubMed
-
- Andersen M, Hanson LG, Madsen KH, Wezel J, Boer V, Van Der Velden T, Van Osch MJP, Klomp D, Webb AG, Versluis MJ. Measuring motion-induced B0-fluctuations in the brain using field probes. Magn. Reson. Med 2016;75:2020–2030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

