Boid Inclusion Body Disease Is Also a Disease of Wild Boa Constrictors
- PMID: 36094085
- PMCID: PMC9602588
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.01705-22
Boid Inclusion Body Disease Is Also a Disease of Wild Boa Constrictors
Abstract
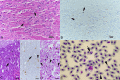
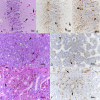
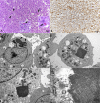
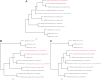
Reptarenaviruses cause boid inclusion body disease (BIBD), a potentially fatal disease, occurring in captive constrictor snakes boas and pythons worldwide. Classical BIBD, characterized by the formation of pathognomonic cytoplasmic inclusion bodies (IBs), occurs mainly in boas, whereas in pythons, for example, reptarenavirus infection most often manifests as central nervous system signs with limited IB formation. The natural hosts of reptarenaviruses are unknown, although free-ranging/wild constrictor snakes are among the suspects. Here, we report BIBD with reptarenavirus infection in indigenous captive and wild boid snakes in Costa Rica using histology, immunohistology, transmission electron microscopy, and next-generation sequencing (NGS). The snakes studied represented diagnostic postmortem cases of captive and wild-caught snakes since 1989. The results from NGS on archival paraffin blocks confirm that reptarenaviruses were already present in wild boa constrictors in Costa Rica in the 1980s. Continuous sequences that were de novo assembled from the low-quality RNA obtained from paraffin-embedded tissue allowed the identification of a distinct pair of reptarenavirus S and L segments in all studied animals; in most cases, reference assembly could recover almost complete segments. Sampling of three prospective cases in 2018 allowed an examination of fresh blood or tissues and resulted in the identification of additional reptarenavirus segments and hartmanivirus coinfection. Our results show that BIBD is not only a disease of captive snakes but also occurs in indigenous wild constrictor snakes in Costa Rica, suggesting boa constrictors to play a role in natural reptarenavirus circulation. IMPORTANCE The literature describes cases of boid inclusion body disease (BIBD) in captive snakes since the 1970s, and in the 2010s, others and ourselves identified reptarenaviruses as the causative agent. BIBD affects captive snakes globally, but the origin and the natural host of reptarenaviruses remain unknown. In this report, we show BIBD and reptarenavirus infections in two native Costa Rican constrictor snake species, and by studying archival samples, we show that both the viruses and the disease have been present in free-ranging/wild snakes in Costa Rica at least since the 1980s. The diagnosis of BIBD in wild boa constrictors suggests that this species plays a role in the circulation of reptarenaviruses. Additional sample collection and analysis would help to clarify this role further and the possibility of, e.g., vector transmission from an arthropod host.
Keywords: arenavirus; boa constrictor; boid inclusion body disease; inclusion body disease; veterinary microbiology; viral pathogenesis; wild snake.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of Reptarenaviruses, Hartmaniviruses, and a Novel Chuvirus in Captive Native Brazilian Boa Constrictors with Boid Inclusion Body Disease.J Virol. 2020 May 18;94(11):e00001-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00001-20. Print 2020 May 18. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32238580 Free PMC article.
-
Reptarenavirus S Segment RNA Levels Correlate with the Presence of Inclusion Bodies and the Number of L Segments in Snakes with Reptarenavirus Infection-Lessons Learned from a Large Breeding Colony.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0506522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.05065-22. Epub 2023 May 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37212675 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Reptarenavirus and Hartmanivirus Infection in Cultured Boid Cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0158522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01585-22. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35862992 Free PMC article.
-
Mammarenavirus Genetic Diversity and Its Biological Implications.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023;439:265-303. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-15640-3_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36592249 Review.
-
Inclusion body disease in snakes: a review and description of three cases in boa constrictors in Belgium.Vet Rec. 2006 Jun 3;158(22):757-60. doi: 10.1136/vr.158.22.757. Vet Rec. 2006. PMID: 16751310 Review.
Cited by
-
Annual (2023) taxonomic update of RNA-directed RNA polymerase-encoding negative-sense RNA viruses (realm Riboviria: kingdom Orthornavirae: phylum Negarnaviricota).J Gen Virol. 2023 Aug;104(8):001864. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001864. J Gen Virol. 2023. PMID: 37622664 Free PMC article.
-
Co-infection of mammarenaviruses in a wild mouse, Tanzania.Virus Evol. 2022 Jul 25;8(2):veac065. doi: 10.1093/ve/veac065. eCollection 2022. Virus Evol. 2022. PMID: 36533140 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of highly virulent mammarenavirus infections-status quo and future directions.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024 May;19(5):537-551. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2024.2340494. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38606475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ever-expanding diversity and complexity of the Arenaviridae family.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2279353. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2279353. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 37968871 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Temperature affects reptarenavirus growth in a permissive host-derived in vitro model.J Gen Virol. 2025 Apr;106(4):002100. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.002100. J Gen Virol. 2025. PMID: 40299760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang L-W, Jacobson ER. 2010. Inclusion body disease, a worldwide infectious disease of boid snakes: a review. J Exotic Pet Med 19:216–225. doi:10.1053/j.jepm.2010.07.014. - DOI
-
- Stenglein MD, Sanders C, Kistler AL, Ruby JG, Franco JY, Reavill DR, Dunker F, Derisi JL. 2012. Identification, characterization, and in vitro culture of highly divergent arenaviruses from boa constrictors and annulated tree boas: candidate etiological agents for snake inclusion body disease. mBio 3:e00180-12. doi:10.1128/mBio.00180-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hetzel U, Sironen T, Laurinmaki P, Liljeroos L, Patjas A, Henttonen H, Vaheri A, Artelt A, Kipar A, Butcher SJ, Vapalahti O, Hepojoki J. 2013. Isolation, identification, and characterization of novel arenaviruses, the etiological agents of boid inclusion body disease. J Virol 87:10918–10935. doi:10.1128/JVI.01123-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stenglein MD, Jacobson ER, Chang LW, Sanders C, Hawkins MG, Guzman DS, Drazenovich T, Dunker F, Kamaka EK, Fisher D, Reavill DR, Meola LF, Levens G, DeRisi JL. 2015. Widespread recombination, reassortment, and transmission of unbalanced compound viral genotypes in natural arenavirus infections. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004900. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004900. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

