A comparison of medium-term heat acclimation by post-exercise hot water immersion or exercise in the heat: adaptations, overreaching, and thyroid hormones
- PMID: 36094449
- PMCID: PMC9602919
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00315.2021
A comparison of medium-term heat acclimation by post-exercise hot water immersion or exercise in the heat: adaptations, overreaching, and thyroid hormones
Abstract
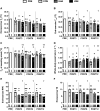
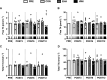
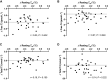
This research compared thermal and perceptual adaptations, endurance capacity, and overreaching markers in men after 3, 6, and 12 days of post-exercise hot water immersion (HWI) or exercise heat acclimation (EHA) with a temperate exercise control (CON), and examined thyroid hormones as a mechanism for the reduction in resting and exercising core temperature (Tre) after HWI. HWI involved a treadmill run at 65% V̇o2peak at 19°C followed by a 40°C bath. EHA and CON involved a work-matched treadmill run at 65% V̇o2peak at 33°C or 19°C, respectively. Compared with CON, resting mean body temperature (Tb), resting and end-exercise Tre, Tre at sweating onset, thermal sensation, and perceived exertion were lower and whole-body sweat rate (WBSR) was higher after 12 days of HWI (all P ≤ 0.049, resting Tb: CON -0.11 ± 0.15°C, HWI -0.41 ± 0.15°C). Moreover, resting Tb and Tre at sweating onset were lower after HWI than EHA (P ≤ 0.015, resting Tb: EHA -0.14 ± 0.14°C). No differences were identified between EHA and CON (P ≥ 0.157) except WBSR that was greater after EHA (P = 0.013). No differences were observed between interventions for endurance capacity or overreaching markers (mood, sleep, Stroop, P ≥ 0.190). Thermal adaptations observed after HWI were not related to changes in thyroid hormone concentrations (P ≥ 0.086). In conclusion, 12 days of post-exercise hot water immersion conferred more complete heat acclimation than exercise heat acclimation without increasing overreaching risk, and changes in thyroid hormones are not related to thermal adaptations after post-exercise hot water immersion.
Keywords: core temperature; hot bath; thermoregulation; thyroxine; triiodothyronine.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Influence of Exercise Heat Acclimation Protocol Characteristics on Adaptation Kinetics: A Quantitative Review With Bayesian Meta-Regressions.Compr Physiol. 2025 Jun;15(3):e70017. doi: 10.1002/cph4.70017. Compr Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40442924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparison of heat acclimation by post-exercise hot water immersion and exercise in the heat.J Sci Med Sport. 2021 Aug;24(8):729-734. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2021.05.008. Epub 2021 May 18. J Sci Med Sport. 2021. PMID: 34116919 Clinical Trial.
-
Post-exercise hot water immersion induces heat acclimation and improves endurance exercise performance in the heat.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2016 Jul;26(7):745-54. doi: 10.1111/sms.12638. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2016. PMID: 26661992 Clinical Trial.
-
Short-term hot water immersion results in substantial thermal strain and partial heat acclimation; comparisons with heat-exercise exposures.J Therm Biol. 2021 Apr;97:102898. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2021.102898. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Therm Biol. 2021. PMID: 33863451 Clinical Trial.
-
Short-term heat acclimation protocols for an aging population: Systematic review.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 2;18(3):e0282038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282038. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36862716 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Influence of Exercise Heat Acclimation Protocol Characteristics on Adaptation Kinetics: A Quantitative Review With Bayesian Meta-Regressions.Compr Physiol. 2025 Jun;15(3):e70017. doi: 10.1002/cph4.70017. Compr Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40442924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional Considerations in Exercise-Based Heat Acclimation: A Narrative Review.Sports Med. 2024 Dec;54(12):3005-3017. doi: 10.1007/s40279-024-02109-x. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 39217233 Review.
-
Look to the stars-Is there anything that public health and rehabilitation can learn from elite sports?Front Sports Act Living. 2023 Jan 23;4:1072154. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2022.1072154. eCollection 2022. Front Sports Act Living. 2023. PMID: 36755563 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Post-exercise hot or cold water immersion does not alter perception of effort or neuroendocrine responses during subsequent moderate-intensity exercise.Exp Physiol. 2024 Sep;109(9):1505-1516. doi: 10.1113/EP091932. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38970776 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Active and Passive Isothermic Heating Leads to Similar Core Temperature Compared With Exercise Alone.J Athl Train. 2025 May 1;60(5):372-380. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-0448.24. J Athl Train. 2025. PMID: 39411876
References
-
- Casa DJ, DeMartini JK, Bergeron MF, Csillan D, Eichner ER, Lopez RM, Ferrara MS, Miller KC, O'Connor F, Sawka MN, Yeargin SW. National athletic trainers' association position statement: exertional heat illnesses. J Athl Train 50: 986–1000, 2015. [Erratum in J Athl Train 52: 401, 2017]. doi:10.4085/1062-6050-52.4.07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

