Pain and masochistic behaviour: The role of descending modulation
- PMID: 36094743
- PMCID: PMC9826249
- DOI: 10.1002/ejp.2037
Pain and masochistic behaviour: The role of descending modulation
Abstract
Background: The mechanisms of pain perception in individuals with masochistic behaviour (MB) remain poorly documented. We hypothesized that MB is associated with context-specific changes in descending pain modulation.
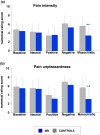
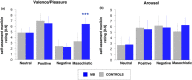
Methods: We compared the effects of four standardized sets of images with positive (erotic), negative (mutilations), masochistic or neutral emotional valences on the RIII nociceptive reflex evoked by electrical stimulation of the sural nerve and recorded on the ipsilateral biceps femoris in 15 controls and 15 men routinely engaging in MB. We systematically assessed the RIII reflex threshold and recruitment curves (up to the tolerance threshold), thermal (heat and cold) pain thresholds measured on the upper and lower limbs and responses to the pain sensitivity questionnaire, to compare basal pain perception between our two groups of participants. We also assessed anxiety, depression, empathy, alexithymia, high sensation seeking and catastrophizing, to investigate their potential influence on the emotional modulation of pain.
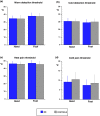
Results: Thermal pain thresholds, RIII reflex recruitment curves, and responses to the psychological and pain sensitivity questionnaires were similar in the two groups. Neutral, positive and negative images modulated the RIII reflex similarly in the two groups. By contrast, masochistic images induced a significant (p < 0.01) decrease in RIII reflex responses in subjects with MB, whereas it tended to increase these responses in control subjects.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that psychological profile, basal pain sensitivity and the emotional modulation of pain are normal in individuals with MB but that these subjects selectively engage descending pain inhibition in the masochistic context.
Significance: Decrease pain perception related to masochistic behaviours is associated with specific activation of descending pain inhibition.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Pain published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Pain Federation - EFIC ®.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest relating to this study to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effect of catastrophizing self-statements on pain perception and the nociceptive flexor reflex (RIII reflex).Clin J Pain. 2013 Aug;29(8):725-32. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e318272ec0c. Clin J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23835766
-
A Randomized Sham-Controlled Cross-Over Study on the Short-Term Effect of Non-Invasive Cervical Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Spinal and Supraspinal Nociception in Healthy Subjects.Headache. 2020 Sep;60(8):1616-1631. doi: 10.1111/head.13891. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Headache. 2020. PMID: 32592516 Clinical Trial.
-
Diffuse analgesic effects of unilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in healthy volunteers.Pain. 2009 Dec 15;147(1-3):224-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.09.016. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Pain. 2009. PMID: 19822394 Clinical Trial.
-
The lower limb flexion reflex in humans.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 Dec;77(6):353-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.11.003. Epub 2005 Dec 28. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16386347 Review.
-
[Clinical exploration of nociception with the use of reflexologic techniques].Neurophysiol Clin. 1990 Nov;20(5):335-56. doi: 10.1016/s0987-7053(05)80203-5. Neurophysiol Clin. 1990. PMID: 1709254 Review. French.
References
-
- Attal, N. , Rouaud, J. , Brasseur, L. , Chauvin, M. , & Bouhassira, D. (2004). Systemic lidocaine in pain due to peripheral nerve injury and predictors of response. Neurology, 62(2), 218–225. - PubMed
-
- Bagby, R. M. , Parker, J. D. A. , & Taylor, G. J. (1994). The twenty‐item Toronto Alexithymia scale‐I. Item selection and cross‐validation of the factor structure. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 38(1), 23–32. - PubMed
-
- Beck, A. T. , Ward, C. H. , Mendelson, M. , Mock, J. , & Erbaugh, J. (1961). An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 4, 561–571. - PubMed
-
- Bossard, A. E. , Guirimand, F. , Fletcher, D. , Gaudé‐Joindreau, V. , Chauvin, M. , & Bouhassira, D. (2002). Interaction of a combination of morphine and ketamine on the nociceptive flexion (RIII) reflex in human volunteers. Pain, 98(1–2), 47–57. - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira, D. , Attal, N. , Willer, J. C. , & Brasseur, L. (1999). Painful and painless peripheral sensory neuropathies due to HIV infection: A comparison using quantitative sensory evaluation. Pain, 1‐2, 265–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

