Neoadjuvant Cemiplimab for Stage II to IV Cutaneous Squamous-Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 36094839
- PMCID: PMC9844515
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2209813
Neoadjuvant Cemiplimab for Stage II to IV Cutaneous Squamous-Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: In a pilot study involving patients with cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma, a high percentage of patients had a pathological complete response with the use of two doses of neoadjuvant cemiplimab before surgery. Data from a phase 2 study are needed to confirm these findings.
Methods: We conducted a phase 2, confirmatory, multicenter, nonrandomized study to evaluate cemiplimab as neoadjuvant therapy in patients with resectable stage II, III, or IV (M0) cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. Patients received cemiplimab, administered at a dose of 350 mg every 3 weeks for up to four doses, before undergoing surgery with curative intent. The primary end point was a pathological complete response (the absence of viable tumor cells in the surgical specimen) on independent review at a central laboratory, with a null hypothesis that a pathological complete response would be observed in 25% of patients. Key secondary end points included a pathological major response (the presence of viable tumor cells that constitute ≤10% of the surgical specimen) on independent review, a pathological complete response and a pathological major response on investigator assessment at a local laboratory, an objective response on imaging, and adverse events.
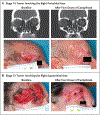
Results: A total of 79 patients were enrolled and received neoadjuvant cemiplimab. On independent review, a pathological complete response was observed in 40 patients (51%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 39 to 62) and a pathological major response in 10 patients (13%; 95% CI, 6 to 22). These results were consistent with the pathological responses determined on investigator assessment. An objective response on imaging was observed in 54 patients (68%; 95% CI, 57 to 78). Adverse events of any grade that occurred during the study period, regardless of whether they were attributed to the study treatment, were observed in 69 patients (87%). Grade 3 or higher adverse events that occurred during the study period were observed in 14 patients (18%).
Conclusions: Neoadjuvant therapy with cemiplimab was associated with a pathological complete response in a high percentage of patients with resectable cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. (Funded by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and Sanofi; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04154943.).
Copyright © 2022 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
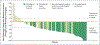
References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global Burden of Disease 2019 results (http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool).
-
- Nehal KS, Bichakjian CK. Update on keratinocyte carcinomas. N Engl J Med 2018;379:363–74. - PubMed
-
- Que SKT, Zwald FO, Schmults CD. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: management of advanced and high-stage tumors. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018;78:249–61. - PubMed
-
- Sweeny L, Zimmerman T, Carroll WR, Schmalbach CE, Day KE, Rosenthal EL. Head and neck cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma requiring parotidectomy: prognostic indicators and treatment selection. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2014;150:610–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
