Novel Isobaric Tagging Reagent Enabled Multiplex Quantitative Glycoproteomics via Electron-Transfer/Higher-Energy Collisional Dissociation (EThcD) Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 36095095
- PMCID: PMC10160164
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.2c00177
Novel Isobaric Tagging Reagent Enabled Multiplex Quantitative Glycoproteomics via Electron-Transfer/Higher-Energy Collisional Dissociation (EThcD) Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
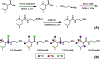
Protein glycosylation, covalent attachment of carbohydrates to polypeptide chains, is a highly important post-translational modification involved in many essential physiological processes. Comprehensive site-specific and quantitative analysis is crucial for revealing the diverse functions and dynamics of glycosylation. To characterize intact glycopeptides, mass spectrometry (MS)-based glycoproteomics employs versatile fragmentation methods, among which electron-transfer/higher-energy collision dissociation (EThcD) has gained great popularity. However, the inherent limitation of EThcD in fragmenting low-charge ions has prevented its widespread applications. Furthermore, there is a need to develop a high-throughput strategy for comparative glycoproteomics with a large cohort of samples. Herein, we developed isobaric N,N-dimethyl leucine-derivatized ethylenediamine (DiLeuEN) tags to increase the charge states of glycopeptides, thereby improving the fragmentation efficiency and allowing for in-depth intact glycopeptide analysis, especially for sialoglycopeptides. Moreover, the unique reporter ions of DiLeuEN-labeled glycopeptides generated in tandem MS spectra enable relative quantification of up to four samples in a single analysis, which represents a new high-throughput method for quantitative glycoproteomics.
Keywords: DiLeuEN; EThcD; isobaric labeling; mass spectrometry; quantitative glycoproteomics.
Figures
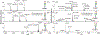

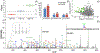
Similar articles
-
[Recent advances in glycopeptide enrichment and mass spectrometry data interpretation approaches for glycoproteomics analyses].Se Pu. 2021 Oct;39(10):1045-1054. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.06011. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34505426 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Electron-Transfer/Higher-Energy Collision Dissociation (EThcD)-Enabled Intact Glycopeptide/Glycoproteome Characterization.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017 Sep;28(9):1751-1764. doi: 10.1007/s13361-017-1701-4. Epub 2017 Jul 10. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017. PMID: 28695533 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific characterization and quantitation of N-glycopeptides in PKM2 knockout breast cancer cells using DiLeu isobaric tags enabled by electron-transfer/higher-energy collision dissociation (EThcD).Analyst. 2018 May 29;143(11):2508-2519. doi: 10.1039/c8an00216a. Analyst. 2018. PMID: 29687791 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Dissociation Methods Differ for N- and O-Glycopeptides.J Proteome Res. 2020 Aug 7;19(8):3286-3301. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00218. Epub 2020 Jun 28. J Proteome Res. 2020. PMID: 32500713 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based fragmentation analysis of glycopeptides.Glycoconj J. 2016 Jun;33(3):261-72. doi: 10.1007/s10719-016-9649-3. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Glycoconj J. 2016. PMID: 26780731 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: An update for 2021-2022.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025 May-Jun;44(3):213-453. doi: 10.1002/mas.21873. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2025. PMID: 38925550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of novel isobaric tags enables accurate and sensitive multiplexed proteomics using complementary ions.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Nov;415(28):6951-6960. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04877-3. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37530794 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput relative quantification of fatty acids by 12-plex isobaric labeling and microchip capillary electrophoresis - Mass spectrometry.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 Aug 22;1318:342905. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342905. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39067909 Free PMC article.
-
6-Plex mdSUGAR Isobaric-Labeling Guide Fingerprint Embedding for Glycomics Analysis.Anal Chem. 2023 Dec 5;95(48):17637-17645. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c03342. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 37982459 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Clinical Glyco(proteo)mics in Precision Medicine.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023 Jun;22(6):100565. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100565. Epub 2023 May 9. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37169080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohtsubo K; Marth JD, Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell 2006, 126 (5), 855–867. - PubMed
-
- Ungar D, Golgi linked protein glycosylation and associated diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol 2009, 20 (7), 762–769. - PubMed
-
- Gudelj I; Lauc G, Protein N-Glycosylation in Cardiovascular Diseases and Related Risk Factors. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep 2018, 12 (6).
-
- Kristic J; Lauc G, Ubiquitous Importance of Protein Glycosylation. In High-Throughput Glycomics and Glycoproteomics: Methods and Protocols, Lauc G; Wuhrer M, Eds. 2017; Vol. 1503, pp 1–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

