First description of the t(3;17)(q27;q21)/IGF2BP2::LSM12 translocation in marginal zone lymphoma
- PMID: 36095303
- PMCID: PMC9811198
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008393
First description of the t(3;17)(q27;q21)/IGF2BP2::LSM12 translocation in marginal zone lymphoma
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
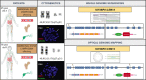

References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Pileri SA, Jaffe ES, Stein HTJ. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2017. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues.
-
- Zucca E, Bertoni F. The spectrum of MALT lymphoma at different sites: biological and therapeutic relevance. Blood. 2016;127(17):2082–2092. - PubMed
-
- Salido M, Baró C, Oscier D, et al. Cytogenetic aberrations and their prognostic value in a series of 330 splenic marginal zone B-cell lymphomas: a multicenter study of the Splenic B-Cell Lymphoma Group. Blood. 2010;116(9):1479–1488. - PubMed
-
- Bonfiglio F, Bruscaggin A, Guidetti F, et al. Genetic and phenotypic attributes of splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Blood. 2022;139(5):732–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

