Small animal photon counting cone-beam CT on a preclinical radiation research platform to improve radiation dose calculation accuracy
- PMID: 36096129
- PMCID: PMC9547611
- DOI: 10.1088/1361-6560/ac9176
Small animal photon counting cone-beam CT on a preclinical radiation research platform to improve radiation dose calculation accuracy
Abstract
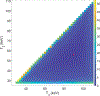
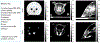
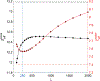
Objective.Cone beam CT (CBCT) in preclinical small animal irradiation platforms provides essential information for image guidance and radiation dose calculation for experiment planning. This project developed a photon-counting detector (PCD)-based multi(3)-energy (ME-)CBCT on a small animal irradiator to improve the accuracy of material differentiation and hence dose calculation, and compared to conventional flat panel detector (FPD)-based CBCT.Approach.We constructed a mechanical structure to mount a PCD to an existing preclinical irradiator platform and built a data acquisition pipeline to acquire x-ray projection data with a 100 kVp x-ray beam using three different energy thresholds in a single gantry rotation. We implemented an energy threshold optimization scheme to determine optimal thresholds to balance signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) among energy channels. Pixel-based detector response calibration was performed to remove ring artifacts in reconstructed CBCT images. Feldkamp-Davis-Kress method was employed to reconstruct CBCT images and a total-variance regularization-based optimization model was used to decompose CBCT images into bone and water material images. We compared dose calculation results using PCD-based ME-CBCT with that of FPD-based CBCT.Main results.The optimal nominal energy thresholds were determined as 26, 56, and 90 keV, under which SNRs in a selected region-of-interest in the water region were 6.11, 5.91 and 5.93 in the three energy channels, respectively. Compared with dose calculation results using FPD-based CBCT, using PCD-based ME-CBCT reduced the mean relative error from 49.5% to 16.4% in bone regions and from 7.5% to 6.9% in soft tissue regions.Significance.PCD-based ME-CBCT is beneficial in improving radiation dose calculation accuracy in experiment planning of preclinical small animal irradiation researches.
Keywords: cone beam CT; photon counting; small animal imaging.
© 2022 Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine.
Figures

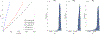

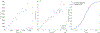


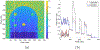
References
-
- Alaei Parham, Gerbi Bruce J, and Geise Richard A. Evaluation of a model-based treatment planning system for dose computations in the kilovoltage energy range. Medical physics, 27(12):2821–2826, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bazalova Magdalena, Carrier Jean-François, Beaulieu Luc, and Verhaegen Frank. Dual-energy ct-based material extraction for tissue segmentation in monte carlo dose calculations. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 53(9):2439, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Boyd Stephen, Boyd Stephen P, and Vandenberghe Lieven. Convex optimization. Cambridge university press, 2004.
-
- Boyd Stephen, Parikh Neal, and Chu Eric. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Now Publishers Inc, 2011.
