HDAC6 Inhibition Reverses Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Hypersensitivity via Tonic Delta Opioid Receptor Signaling
- PMID: 36096670
- PMCID: PMC9617617
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1182-22.2022
HDAC6 Inhibition Reverses Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Hypersensitivity via Tonic Delta Opioid Receptor Signaling
Abstract
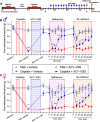
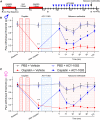
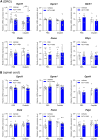
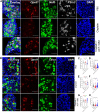
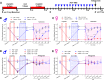
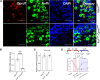
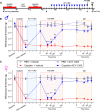
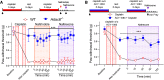
Peripheral neuropathic pain induced by the chemotherapeutic cisplatin can persist for months to years after treatment. Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) inhibitors have therapeutic potential for cisplatin-induced neuropathic pain since they persistently reverse mechanical hypersensitivity and spontaneous pain in rodent models. Here, we investigated the mechanisms underlying reversal of mechanical hypersensitivity in male and female mice by a 2 week treatment with an HDAC6 inhibitor, administered 3 d after the last dose of cisplatin. Mechanical hypersensitivity in animals of both sexes treated with the HDAC6 inhibitor was temporarily reinstated by a single injection of the neutral opioid receptor antagonist 6β-naltrexol or the peripherally restricted opioid receptor antagonist naloxone methiodide. These results suggest that tonic peripheral opioid ligand-receptor signaling mediates reversal of cisplatin-induced mechanical hypersensitivity after treatment with an HDAC6 inhibitor. Pointing to a specific role for δ opioid receptors (DORs), Oprd1 expression was decreased in DRG neurons following cisplatin administration, but normalized after treatment with an HDAC6 inhibitor. Mechanical hypersensitivity was temporarily reinstated in both sexes by a single injection of the DOR antagonist naltrindole. Consistently, HDAC6 inhibition failed to reverse cisplatin-induced hypersensitivity when DORs were genetically deleted from advillin+ neurons. Mechanical hypersensitivity was also temporarily reinstated in both sexes by a single injection of a neutralizing antibody against the DOR ligand met-enkephalin. In conclusion, we reveal that treatment with an HDAC6 inhibitor induces tonic enkephalin-DOR signaling in peripheral sensory neurons to suppress mechanical hypersensitivity.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Over one-fourth of cancer survivors suffer from intractable painful chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), which can last for months to years after treatment ends. HDAC6 inhibition is a novel strategy to reverse CIPN without negatively interfering with tumor growth, but the mechanisms responsible for persistent reversal are not well understood. We built on evidence that the endogenous opioid system contributes to the spontaneous, apparent resolution of pain caused by nerve damage or inflammation, referred to as latent sensitization. We show that blocking the δ opioid receptor or its ligand enkephalin unmasks CIPN in mice treated with an HDAC6 inhibitor (latent sensitization). Our work provides insight into the mechanisms by which treatment with an HDAC6 inhibitor apparently reverses CIPN.
Keywords: CIPN; allodynia; latent sensitization; opioid receptors.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang et al.
Figures
References
-
- Abdallah K, Gendron L (2018) The delta opioid receptor in pain control. Handb Exp Pharmacol 247:147–177. - PubMed
-
- Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F, Rocha K, Kumaraswamy S, Boyapalle S, Atadja P, Seto E, Bhalla K (2005) Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 280:26729–26734. 10.1074/jbc.C500186200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bardoni R, Tawfik VL, Wang D, Francois A, Solorzano C, Shuster SA, Choudhury P, Betelli C, Cassidy C, Smith K, de Nooij JC, Mennicken F, O'Donnell D, Kieffer BL, Woodbury CJ, Basbaum AI, MacDermott AB, Scherrer G (2014) Delta opioid receptors presynaptically regulate cutaneous mechanosensory neuron input to the spinal cord dorsal horn. Neuron 81:1312–1327. 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.044 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
