What is the global prevalence of depression among men who have sex with men? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36096814
- PMCID: PMC9465955
- DOI: 10.1186/s12991-022-00414-1
What is the global prevalence of depression among men who have sex with men? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Depression due to stigma resulting from their sexual identity, isolation, social exclusion, and insufficient access to care and counseling services has become a health problem among men who have sex with men (MSM).
Objectives: This study aimed to determine the global prevalence of depression among MSM as a systematic review and meta-analysis.
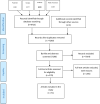
Methods: This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis performed in five steps of search strategy, screening and selecting articles, data extraction, evaluation of the risk of bias, and meta-analysis. In this study, the determined keywords were searched in the databases of PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Web of Science from January 1913 to July 2021 to find the initial articles, from which data were extracted according to the set checklist in the data extraction stage. Finally, the studies were included in the present meta-analysis according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, to be evaluated using the Newcastle Ottawa scale checklist. I Square and Q Cochrane were also used to assess the degree of heterogeneity. The analyses were performed using the random-effects model in STATA 16.
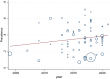
Results: The results showed the quality score of the majority of cross-sectional studies included in the meta-analysis (62 studies) was equal to six or seven (moderate), and five ones had a high-quality score. After combining these studies, the pooled prevalence of depression among MSM in the world was 35% (95% CI 31%-39%, I square; 98.95%, P-value < 0.001). Population subgroup analysis showed the pooled prevalence of depression among MSM living with HIV was 47% (95% CI 39%-55%, I square; 95.76%, P-value < 0.001). Continent subgroup analysis showed the highest pooled prevalence of depression among Asian MSM at 37% (95% CI 31%-43%, I square; 99.07%, P-value < 0.001). Also, in the subgroup analysis of the sampling method, the pooled prevalence in the studies which used the respondent-driven sampling method was equal to 34% (95% CI 25%-43%, I square; 99.32%, P-value < 0.001). Sensitivity analysis revealed the pooled prevalence of depression in studies included in the meta-analysis was near or around the pooled estimate.
Conclusion: The pooled prevalence of depression among MSM was almost three times higher than the general male population. Therefore, particular and therapeutic interventions such as screening, and harm reduction programs for mental disorders, especially depression, are suggested to be considered in service packages.
Keywords: Depression; Global prevalence; MSM; Men who have sex with men; Meta-analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prevalence of hepatitis B and C infections among HIV-positive men who have sex with men: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 26;7(6):e2206. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.2206. eCollection 2024 Jun. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38933421 Free PMC article.
-
The global prevalence of suicidal ideation and suicide attempts among men who have sex with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Sep 21;28(1):361. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01338-6. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37735701 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of depression in men who have sex with men (MSM) living with HIV: A meta-analysis of comparative and epidemiological studies.Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2020 Sep-Oct;66:112-119. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.04.001. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32818791
-
Reported prevalence of depression or depressive symptoms among men who have sex with men in China, 2004-2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Affect Disord. 2020 Dec 1;277:192-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.08.011. Epub 2020 Aug 14. J Affect Disord. 2020. PMID: 32829195
-
Lifetime prevalence of suicidal ideation among men who have sex with men: a meta-analysis.BMC Psychiatry. 2017 Dec 21;17(1):406. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1575-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 29268723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Global trends in depression among patients living with HIV: A bibliometric analysis.Front Psychol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1125300. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1125300. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36968702 Free PMC article.
-
Loneliness and depressive symptoms among men who have sex with men in China: A cross-sectional study.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 6;14:1179703. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1179703. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37091698 Free PMC article.
-
Stigma and other correlates of self-esteem and depression in cisgender men and transfeminine persons with HIV who have sex with men in Kenya, Malawi, and South Africa (HPTN 075).AIDS Care. 2025 Jul;37(7):1181-1193. doi: 10.1080/09540121.2025.2488874. Epub 2025 Jun 5. AIDS Care. 2025. PMID: 40469020 Free PMC article.
-
A Study of the Relationship between Men Who Have Sex with Men Stigma and Depression: A Moderated Mediation Model.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 29;11(21):2849. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11212849. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37957994 Free PMC article.
-
University students who were men who had sex with men (MSM) in Sichuan, China had a higher prevalence of insomnia and probable depression than their non-MSM counterparts: mediation via emotional dysregulations.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Nov 12;24(1):793. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06192-2. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39533253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desyani NLJ, Waluyo A, Yona SJE. The relationship between stigma, religiosity, and the quality of life of HIV-positive MSM in Medan Indonesia. Enfermeria-clinica. 2019;29:510–514. doi: 10.1016/j.enfcli.2019.04.077. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

