A critical overview of current progress for COVID-19: development of vaccines, antiviral drugs, and therapeutic antibodies
- PMID: 36096815
- PMCID: PMC9465653
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-022-00852-9
A critical overview of current progress for COVID-19: development of vaccines, antiviral drugs, and therapeutic antibodies
Abstract
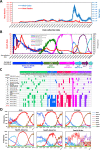
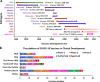
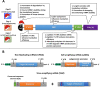
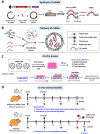
The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic remains a global public health crisis, presenting a broad range of challenges. To help address some of the main problems, the scientific community has designed vaccines, diagnostic tools and therapeutics for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. The rapid pace of technology development, especially with regard to vaccines, represents a stunning and historic scientific achievement. Nevertheless, many challenges remain to be overcome, such as improving vaccine and drug treatment efficacies for emergent mutant strains of SARS-CoV-2. Outbreaks of more infectious variants continue to diminish the utility of available vaccines and drugs. Thus, the effectiveness of vaccines and drugs against the most current variants is a primary consideration in the continual analyses of clinical data that supports updated regulatory decisions. The first two vaccines granted Emergency Use Authorizations (EUAs), BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273, still show more than 60% protection efficacy against the most widespread current SARS-CoV-2 variant, Omicron. This variant carries more than 30 mutations in the spike protein, which has largely abrogated the neutralizing effects of therapeutic antibodies. Fortunately, some neutralizing antibodies and antiviral COVID-19 drugs treatments have shown continued clinical benefits. In this review, we provide a framework for understanding the ongoing development efforts for different types of vaccines and therapeutics, including small molecule and antibody drugs. The ripple effects of newly emergent variants, including updates to vaccines and drug repurposing efforts, are summarized. In addition, we summarize the clinical trials supporting the development and distribution of vaccines, small molecule drugs, and therapeutic antibodies with broad-spectrum activity against SARS-CoV-2 strains.
Keywords: COVID-19; Neutralizing antibodies; SARS-CoV-2; Small molecule antiviral drugs; Therapeutics; Vaccine development; mRNA vaccines.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. August 16, 2022. WHO coronavirus dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

