Relationship between ER expression by IHC or mRNA with Ki67 response to aromatase inhibition: a POETIC study
- PMID: 36096872
- PMCID: PMC9466340
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-022-01556-6
Relationship between ER expression by IHC or mRNA with Ki67 response to aromatase inhibition: a POETIC study
Abstract
Background: In clinical practice, oestrogen receptor (ER) analysis is almost entirely by immunohistochemistry (IHC). ASCO/CAP recommends cut-offs of < 1% (negative) and 1-10% (low) cells positive. There is uncertainty whether patients with ER low tumours benefit from endocrine therapy. We aimed to assess IHC and mRNA cut-points for ER versus biological response of primary breast cancer to 2 weeks' aromatase inhibitor treatment as measured by change in Ki67.
Methods: Cases were selected from the aromatase inhibitor treatment group of POETIC. We selected the 15% with the poorest Ki67 response (PR, < 40% Ki67 suppression, n = 230) and a random 30% of the remainder categorised as intermediate (IR, 40-79% Ki67 suppression, n = 150) and good-responders (GR, ≥ 80% Ki67 suppression, n = 230) from HER2 - group. All HER2 + cases available were selected irrespective of their response category (n = 317). ER expression was measured by IHC and qPCR.
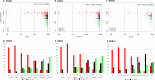
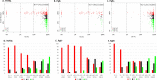
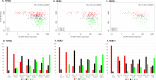
Results: ER IHC was available from 515 HER2 - and 186 HER2 + tumours and ER qPCR from 367 HER2 - and 171 HER2 + tumours. Ninety-one percentage of patients with ER IHC < 10% were PRs with similar rates in HER2 - and HER2 + cases. At or above ER IHC 10% substantial numbers of patients showed IR or GR. Similar proportions of patients were defined by cut-points of ER IHC < 10% and ER mRNA < 5 units. In addition, loss of PgR expression altered ER anti-proliferation response with 92% of PgR - cases with ER IHC < 40% being PRs.
Conclusions: There was little responsiveness at IHC < 10% and no distinction between < 1% and 1-10% cells positive. Similar separation of PRs from IR/GRs was achieved by IHC and mRNA.
Keywords: Aromatase inhibitors; Breast cancer; ESR1; Ki67; PgR.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.C.U.C. has a patent for Breast Cancer Classifier: US Patent No. 9,631,239 with royalties paid and receive research funding from NanoString Technologies and veracyte advisory role. MD receives honoraria from Myriad Genetics and is a consultant and advisory board member of GTx, Radius Health, Orion Pharma, Lilly, Agile and Astrazeneca, has received funding from Pfizer (Inst) and Radius Health (Inst) and has been paid expenses from Pfizer and Myriad Genetics. JMB reports grants from Cancer Research UK, during the conduct of the study; grants from Medivation; grants and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Puma Biotechnology, Clovis Oncology, Pfizer, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Roche, outside the submitted work. LK reports grants from Cancer Research UK, during the conduct of the study. HT received salary from Bayer. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group Aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen in early breast cancer: patient-level meta-analysis of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2015;386:10001. - PubMed
-
- Wolff AC, Dowsett M. Estrogen receptor: a never ending story? J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:22. - PubMed
-
- Foekens JA, Portengen H, van Putten WL, Peters HA, Krijnen HL, Alexieva-Figusch J, et al. Prognostic value of estrogen and progesterone receptors measured by enzyme immunoassays in human breast tumor cytosols. Cancer Res. 1989;49:21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

