Development of a short-form Chinese health literacy scale for low salt consumption (CHLSalt-22) and its validation among hypertensive patients
- PMID: 36096877
- PMCID: PMC9465139
- DOI: 10.1186/s40795-022-00594-9
Development of a short-form Chinese health literacy scale for low salt consumption (CHLSalt-22) and its validation among hypertensive patients
Abstract
Background: With the accelerated pace of people's life and the changing dietary patterns, the number of chronic diseases is increasing and occurring at a younger age in today's society. The speedily rising hypertensive patients have become one of the main risk factors for chronic diseases. People should focus on health literacy related to salt consumption and reach a better quality of life. Currently, there is a lack of local assessment tools for low salt consumption in mainland China.
Objective: To develop a short-form version of the Chinese Health Literacy Scale For Low Salt Consumption instrument for use in mainland China.
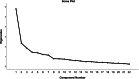
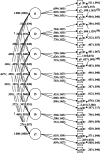
Methods: A cross-sectional design was conducted on a sample of 1472 people in Liaoxi, China. Participants completed a sociodemographic questionnaire, the Chinese version of the CHLSalt-22, the measuring change in restriction of salt (sodium) in the diet in hypertensives (MCRSDH-SUST), the Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire (BIPQ), and the Benefit-Finding Scales (BFS) to test the hypothesis. Exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory factor analyses were performed to examine the underlying factor structure of the CHLSalt-22. One month later, 37 patients who participated in the first test were recruited to evaluate the test-retest reliability.
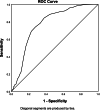
Results: The CHLSalt-22 demonstrated adequate internal consistency, good test-retest reliability, satisfactory construct validity, convergent validity and discriminant validity. The CHLSalt-22 count scores were correlated with age, sex, body mass index (BMI), education level, income, occupation, the Measuring Change in Restriction of Salt (sodium) in Diet in Hypertensives (MCRSDH-SUST), the Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire (BIPQ), and the Benefit-Finding Scales (BFS).
Conclusion: The results indicate that the Chinese Health Literacy Scale For Low Salt Consumption (CHLSalt-22) version has good reliability and validity and can be considered a tool to assess health literacy related to salt consumption in health screenings.
Keywords: Health literacy; Hypertensive patients; Low salt; Revision and application; Scale.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of Chinese Health Literacy Scale for Low Salt Consumption-Hong Kong Population (CHLSalt-HK).PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132303. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132303. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26148008 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development and validation of the reproductive health literacy questionnaire for Chinese unmarried youth.Reprod Health. 2021 Nov 13;18(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01278-6. Reprod Health. 2021. PMID: 34774064 Free PMC article.
-
Translation of the Chinese version of the modified Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 and its validation among college students.J Eat Disord. 2021 Sep 16;9(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s40337-021-00471-z. J Eat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34530921 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a Chinese parental health literacy questionnaire for caregivers of children 0 to 3 years old.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Aug 22;19(1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1670-9. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31438889 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-cultural adaptation and psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the postpartum depression literacy scale.Front Psychol. 2022 Aug 9;13:966770. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.966770. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36017447 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Psychometric testing of the Determinants of Salt-Restriction Behaviour Questionnaire in people of Chinese ancestry: a methodological study.BMC Nurs. 2022 Dec 2;21(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s12912-022-01124-5. BMC Nurs. 2022. PMID: 36461075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tu WJ, Zeng X, Liu Q. Aging tsunami coming: the main finding from China's seventh national population census. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021. 10.1007/s40520-021-02017-4. - PubMed
-
- National Bureau of statistics of the People's Republic of China. Statistical Bulletin on National Economic and Social Development (2020), 2021(3): 8–22.
-
- NCD risk factor collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398(10304):957–80. 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
