Reactivating hippocampal-mediated memories during reconsolidation to disrupt fear
- PMID: 36096993
- PMCID: PMC9468169
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32246-8
Reactivating hippocampal-mediated memories during reconsolidation to disrupt fear
Abstract
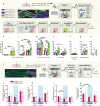
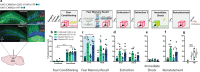
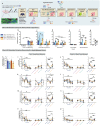
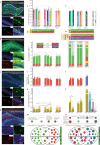
Memories are stored in the brain as cellular ensembles activated during learning and reactivated during retrieval. Using the Tet-tag system in mice, we label dorsal dentate gyrus neurons activated by positive, neutral or negative experiences with channelrhodopsin-2. Following fear-conditioning, these cells are artificially reactivated during fear memory recall. Optical stimulation of a competing positive memory is sufficient to update the memory during reconsolidation, thereby reducing conditioned fear acutely and enduringly. Moreover, mice demonstrate operant responding for reactivation of a positive memory, confirming its rewarding properties. These results show that interference from a rewarding experience can counteract negative affective states. While memory-updating, induced by memory reactivation, involves a relatively small set of neurons, we also find that activating a large population of randomly labeled dorsal dentate gyrus neurons is effective in promoting reconsolidation. Importantly, memory-updating is specific to the fear memory. These findings implicate the dorsal dentate gyrus as a potential therapeutic node for modulating memories to suppress fear.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

