A bacterial pan-genome makes gene essentiality strain-dependent and evolvable
- PMID: 36097170
- PMCID: PMC9519441
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-022-01208-7
A bacterial pan-genome makes gene essentiality strain-dependent and evolvable
Abstract
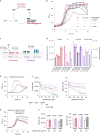
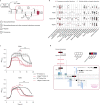
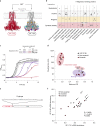
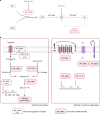
Many bacterial species are represented by a pan-genome, whose genetic repertoire far outstrips that of any single bacterial genome. Here we investigate how a bacterial pan-genome might influence gene essentiality and whether essential genes that are initially critical for the survival of an organism can evolve to become non-essential. By using Transposon insertion sequencing (Tn-seq), whole-genome sequencing and RNA-seq on a set of 36 clinical Streptococcus pneumoniae strains representative of >68% of the species' pan-genome, we identify a species-wide 'essentialome' that can be subdivided into universal, core strain-specific and accessory essential genes. By employing 'forced-evolution experiments', we show that specific genetic changes allow bacteria to bypass essentiality. Moreover, by untangling several genetic mechanisms, we show that gene essentiality can be highly influenced by and/or be dependent on: (1) the composition of the accessory genome, (2) the accumulation of toxic intermediates, (3) functional redundancy, (4) efficient recycling of critical metabolites and (5) pathway rewiring. While this functional characterization underscores the evolvability potential of many essential genes, we also show that genes with differential essentiality remain important antimicrobial drug target candidates, as their inactivation almost always has a severe fitness cost in vivo.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Comment in
-
Gene essentiality evolves across a pangenome.Nat Microbiol. 2022 Oct;7(10):1510-1511. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01231-8. Nat Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36097169 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rancati G, Moffat J, Typas A, Pavelka N. Emerging and evolving concepts in gene essentiality. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018;19:34–49. - PubMed
-
- Shields RC, Jensen PA. The bare necessities: uncovering essential and condition-critical genes with transposon sequencing. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2019;34:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Juhas M, Eberl L, Church GM. Essential genes as antimicrobial targets and cornerstones of synthetic biology. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30:601–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

