Post-infusion CAR TReg cells identify patients resistant to CD19-CAR therapy
- PMID: 36097223
- PMCID: PMC10917089
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01960-7
Post-infusion CAR TReg cells identify patients resistant to CD19-CAR therapy
Abstract
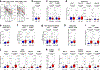
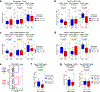
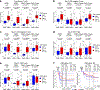
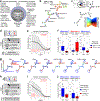
Approximately 60% of patients with large B cell lymphoma treated with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies targeting CD19 experience disease progression, and neurotoxicity remains a challenge. Biomarkers associated with resistance and toxicity are limited. In this study, single-cell proteomic profiling of circulating CAR T cells in 32 patients treated with CD19-CAR identified that CD4+Helios+ CAR T cells on day 7 after infusion are associated with progressive disease and less severe neurotoxicity. Deep profiling demonstrated that this population is non-clonal and manifests hallmark features of T regulatory (TReg) cells. Validation cohort analysis upheld the link between higher CAR TReg cells with clinical progression and less severe neurotoxicity. A model combining expansion of this subset with lactate dehydrogenase levels, as a surrogate for tumor burden, was superior for predicting durable clinical response compared to models relying on each feature alone. These data credential CAR TReg cell expansion as a novel biomarker of response and toxicity after CAR T cell therapy and raise the prospect that this subset may regulate CAR T cell responses in humans.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











Comment in
-
CAR Treg cells: prime suspects in therapeutic resistance.Nat Med. 2022 Sep;28(9):1755-1756. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01998-7. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 36109644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson JS, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet 396, 839–852 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Schuster SJ, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 380, 45–56 (2019). - PubMed
References (Methods only)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

