Manufacturing-dependent change in biological activity of the TLR4 agonist GSK1795091 and implications for lipid A analog development
- PMID: 36097345
- PMCID: PMC9652439
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.13387
Manufacturing-dependent change in biological activity of the TLR4 agonist GSK1795091 and implications for lipid A analog development
Abstract
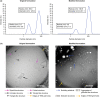
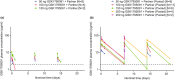
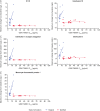
A phase I trial (NCT03447314; 204686) evaluated the safety and efficacy of GSK1795091, a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) agonist, in combination with immunotherapy (GSK3174998 [anti-OX40 monoclonal antibody], GSK3359609 [anti-ICOS monoclonal antibody], or pembrolizumab) in patients with solid tumors. The primary endpoint was safety; other endpoints included efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics (PD). Manufacturing of GSK1795091 formulation was modified during the trial to streamline production and administration, resulting in reduced PD (cytokine) activity. Fifty-four patients received GSK1795091 with a combination partner; 32 received only the modified GSK1795091 formulation, 15 received only the original formulation, and seven switched mid-study from the original to the modified formulation. Despite the modified formulation demonstrating higher systemic GSK1795091 exposure compared with the original formulation, the transient, dose-dependent elevations in cytokine and chemokine concentrations were no longer observed (e.g., IP-10, IL10, IL1-RA). Most patients (51/54; 94%) experienced ≥1 treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) during the study. Safety profiles were similar between formulations, but a higher incidence of TEAEs associated with immune responses (chills, fatigue, pyrexia, nausea, and vomiting) were observed with the original formulation. No conclusions can be made regarding GSK1795091 anti-tumor activity due to the limited data collected. Manufacturing changes were hypothesized to have caused the change in biological activity in this study. Structural characterization revealed GSK1795091 aggregate size in the modified formulation to be twice that in the original formulation, suggesting a negative correlation between GSK1795091 aggregate size and PD activity. This may have important clinical implications for future development of structurally similar compounds.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
A.R.H. received research funding (paid to institution) from GSK, Merck, Pfizer, MedImmune/Genentech, Roche, Janssen, BMS, AstraZeneca, Astellas, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, and Bayer; and provided consultation or attended advisory boards for GSK, Merck, Novartis, and Eisai. G.C., H.S., J.C., K.M., M.A., M.L.W., and R.E. are employed by GSK and hold GSK stock/shares. C.M. and P.S. are former employees of GSK. E.G. receives research funding from Novartis, Roche, Thermo Fisher, AstraZeneca, Taiho, and BeiGene; is a consultant/advisor for Roche/Genentech, F. Hoffmann/La Roche, Ellipses Pharma, Neomed Therapeutics 1 Inc., Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Global Service, SeaGen, Alkermes, Thermo Fisher, Bristol Myers Squibb, MabDiscovery, Anaveon, and F‐Star Therapeutics; has taken part in the speakers bureau for Merck Sharp & Dohme, Roche, Thermo Fisher, and Lilly; is a clinical trial principal investigator (PI) or co‐PI on studies carried out by Affimed Gmbh, Amgen SA, Anaveon AG, AstraZeneca AB, Biontech Gmbh, Catalym Gmbh, Cytomx, F. Hoffmann La Roche Ltd, F‐Star Beta Limited, Genentech Inc, Genmab B.V., Hutchison Medipharma Limited, Icon, Imcheck Therapeutics, Immunocore Ltd, Janssen‐Cilag SA, Medimmune Llc, Merck Kgga, Novartis Farmacéutica, S. A., Peptomyc, Ribon Therapeutics, Roche Farma S.A., Seattle Genetics Inc, Symphogen A/S, and Taiho Pharma USA Inc. N.S. provided consultation or attended advisory boards for AIMM Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Ellipses Pharma; received institutional research funding from AB Science, Abbvie, Actuate Therapeutics, Amgen, Array, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bayer, Blueprint Medicines, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cantargia, CellCentric, Cytovation, Deciphera, Genentech/Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Incyte, Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Merus, Molecular Partners, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sanofi, Taiho, and Takeda (outside the submitted work). G.J.H. receives consulting fees and serves in an advisory role for Bicara, Boxer Capital, BMS, Exicure, General Catalyst, Kura, Maverick, Merck, Naveris, Prelude, Rain, Regeneron/Sanofi Genzyme, Remix, and SIRPant. He receives institutional grant support from Actuate, ASCO Conquer Cancer Foundation, Bicara, BMS, Elevar, Exicure, Gateway for Cancer Research, Genentech, GSK, Kartos, Kite, KSQ, NantKwest/Altor Bioscience, Regeneron, Repertoire, Sanofi Genzyme, Secura Bio, and V Foundation/ACCRF. Expert witness role: Aaronson Rappaport Feinstein & Deutsch, LLP; Ahmuty, Demers, & McManus, Esqs; and Wilson Elser Moskowitz Edelman & Dicker, LLP. H.P. received research/grant funding from the following sources: Adlai Nortye USA, Alpine Immune Sciences, Ambrx, Amgen, Aprea Therapeutics AB, Array BioPharma, Bayer, BeiGene, BJ Bioscience, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Elicio Therapeutics, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Gossamer Bio, Hoffman‐LaRoche, Hutchison MediPharma, ImmuneOncia Therapeutics, Incyte, Jounce Therapeutics, Mabspace Biosciences, MacroGenics, MedImmune, Medivation, Merck, Millennium, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Oncologie, Pfizer, PsiOxus Therapeutics, Puma Biotechnology, Regeneron, Pharmaceuticals, RePare Therapeutics, Seattle Genetics, Synermore Biologics, Taiho Pharmaceutical, TopAlliance Biosciences, Turning Point Therapeutics, Vedanta Biosciences, and Xencor Inc. J.S. has a leadership role at Dialectic Therapeutics and owns stocks and other ownership interests at Abbvie, Abbott Laboratories, Bristol Myers Squibb, Intuitive Surgical, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Regeneron; has consulting or advisory roles at Synlogic and Binhui Biopharmaceuticals, Ltd. S.A.P.P. receives research/grant funding through the institution from the following sources: AbbVie, Inc.; ABM Therapeutics, Inc.; Acepodia, Inc.; Alkermes; Aminex Therapeutics; Amphivena Therapeutics, Inc.; BioMarin Pharmaceutical, Inc.; Boehringer Ingelheim; Bristol Myers Squibb; Cerulean Pharma, Inc.; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd; Curis, Inc.; Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals; Daiichi Sankyo; Eli Lilly; ENB Therapeutics; Five Prime Therapeutics; F‐Star Beta Limited; F‐Star Therapeutics; Gene Quantum; Genmab A/S; GlaxoSmithKline; Helix BioPharma Corp.; HiberCell, Inc.; Immunomedics, Inc.; Incyte Corp.; Jacobio Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd; Lytix Biopharma AS; Medimmune, LLC; Medivation, Inc.; Merck Sharp and Dohme Corp.; Novartis Pharmaceuticals; Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Pfizer; Principia Biopharma, Inc.; Puma Biotechnology, Inc.; Rapt Therapeutics, Inc.; Seattle Genetics; Silverback Therapeutics; Synlogic Therapeutics; Taiho Oncology; Tesaro, Inc.; TransThera Bio; NCI/NIH; P30CA016672 – Core Grant (CCSG Shared Resources). She has worked as a consultant for CRC Oncology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of the TLR4 Agonist GSK1795091 in Healthy Individuals: Results from a Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Ascending Dose Study.Clin Ther. 2020 Aug;42(8):1519-1534.e33. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.05.022. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 32739049 Clinical Trial.
-
First-in-human phase I study of the OX40 agonist GSK3174998 with or without pembrolizumab in patients with selected advanced solid tumors (ENGAGE-1).J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Mar;11(3):e005301. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005301. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36927527 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1/2 study of intratumoral G100 (TLR4 agonist) with or without pembrolizumab in follicular lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2022 Apr;63(4):821-833. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2021.2010057. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Leuk Lymphoma. 2022. PMID: 34865586 Clinical Trial.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 14;12(12):CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 30;4:CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub3. PMID: 33316104 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
A Bibliometric Analysis on Multi-epitope Vaccine Development Against SARS-CoV-2: Current Status, Development, and Future Directions.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 9. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01358-5. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39789401 Review.
-
"Open Sesame" to the complexity of pattern recognition receptors of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 22;14:1130060. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1130060. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engaging stimulatory immune checkpoint interactions in the tumour immune microenvironment of primary liver cancers - how to push the gas after having released the brake.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 19;15:1357333. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1357333. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38440738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications and clinical trial landscape using Toll-like receptor agonists to reduce the toll of cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023 Mar 8;7(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00364-1. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36890302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the performance of macrophages in tumour microenvironment: a call for precision immunotherapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jun 11;17(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01559-0. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38863020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El‐Zayat SR, Sibaii H, Mannaa FA. Toll‐like receptors activation, signaling, and targeting: an overview. Bulletin of the National Research Centre. 2019;43(1):187. doi:10.1186/s42269-019-0227-2 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

