Regional importation and asymmetric within-country spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the Netherlands
- PMID: 36097810
- PMCID: PMC9470152
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.78770
Regional importation and asymmetric within-country spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the Netherlands
Abstract
Background: Variants of concern (VOCs) of SARS-CoV-2 have caused resurging waves of infections worldwide. In the Netherlands, the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta VOCs circulated widely between September 2020 and August 2021. We sought to elucidate how various control measures, including targeted flight restrictions, had impacted the introduction and spread of these VOCs in the Netherlands.
Methods: We performed phylogenetic analyses on 39,844 SARS-CoV-2 genomes collected under the Dutch national surveillance program.
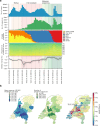
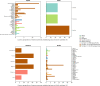
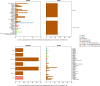
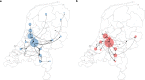
Results: We found that all four VOCs were introduced before targeted flight restrictions were imposed on countries where the VOCs first emerged. Importantly, foreign introductions, predominantly from other European countries, continued during these restrictions. After their respective introductions into the Netherlands, the Alpha and Delta VOCs largely circulated within more populous regions of the country with international connections before asymmetric bidirectional transmissions occurred with the rest of the country and the VOC became the dominant circulating lineage.
Conclusions: Our findings show that flight restrictions had limited effectiveness in deterring VOC introductions due to the strength of regional land travel importation risks. As countries consider scaling down SARS-CoV-2 surveillance efforts in the post-crisis phase of the pandemic, our results highlight that robust surveillance in regions of early spread is important for providing timely information for variant detection and outbreak control.
Funding: None.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; epidemiology; global health; infectious disease; microbiology; public health; viruses.
© 2022, Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AH, EK, JK, HV, KH, AK, Iv, DK, JW, CR, DE, CR No competing interests declared
Figures


Update of
-
Regional importation and asymmetric within-country spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the Netherlands.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Mar 22:2022.03.21.22272611. doi: 10.1101/2022.03.21.22272611. medRxiv. 2022. Update in: Elife. 2022 Sep 13;11:e78770. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78770. PMID: 35350194 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Aksamentov I, Roemer C, Hodcroft EB, Neher RA. Nextclade: clade assignment, mutation calling and quality control for viral genomes. Journal of Open Source Software. 2021;6:3773. doi: 10.21105/joss.03773. - DOI
-
- Artic Network Artic Network Protocols. 2020. [July 20, 2022]. https://artic.network/2-protocols.html
-
- Brauner JM, Mindermann S, Sharma M, Johnston D, Salvatier J, Gavenčiak T, Stephenson AB, Leech G, Altman G, Mikulik V, Norman AJ, Monrad JT, Besiroglu T, Ge H, Hartwick MA, Teh YW, Chindelevitch L, Gal Y, Kulveit J. Inferring the effectiveness of government interventions against COVID-19. Science. 2021;371:eabd9338. doi: 10.1126/science.abd9338. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brito AF, Semenova E, Dudas G, Hassler GW, Kalinich CC, Kraemer MUG, Ho J, Tegally H, Githinji G, Agoti CN, Matkin LE, Whittaker C, Howden BP, Sintchenko V, Zuckerman NS, Mor O, Blankenship HM, de Oliveira T, Lin RTP, Siqueira MM, Resende PC, Vasconcelos ATR, Spilki FR, Aguiar RS, Alexiev I, Ivanov IN, Philipova I, Carrington CVF, Sahadeo NSD, Gurry C, Maurer-Stroh S, Naidoo D, von Eije KJ, Perkins MD, van Kerkhove M, Hill SC, Sabino EC, Pybus OG, Dye C, Bhatt S, Flaxman S, Suchard MA, Grubaugh ND, Baele G, Faria NR, Danish Covid-19 Genome Consortium. COVID-19 Impact Project. Network for Genomic Surveillance in South Africa. GISAID core curation team Global Disparities in SARS-Cov-2 Genomic Surveillance. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.08.21.21262393. - DOI
-
- Campbell F, Archer B, Laurenson-Schafer H, Jinnai Y, Konings F, Batra N, Pavlin B, Vandemaele K, Kerkhove MD, Jombart T, Morgan O, Waroux OLP. Increased transmissibility and global spread of sarscov- 2 variants of concern as at june 2021. Eurosurveillance. 2021;26:1–6. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.24.2100509/CITE/PLAINTEXT. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

