Pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors to combat COVID-19 and other emerging coronavirus infectious diseases
- PMID: 36098460
- PMCID: PMC9539121
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.28143
Pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors to combat COVID-19 and other emerging coronavirus infectious diseases
Abstract
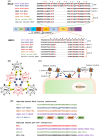
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of the currently ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, has posed a serious threat to global public health. Recently, several SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs) have emerged and caused numerous cases of reinfection in convalescent COVID-19 patients, as well as breakthrough infections in vaccinated individuals. This calls for the development of broad-spectrum antiviral drugs to combat SARS-CoV-2 and its VOCs. Pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors, targeting the conserved heptad repeat 1 (HR1) in spike protein S2 subunit, can broadly and potently inhibit infection of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, as well as other human coronaviruses. In this review, we summarized the most recent development of pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors, such as EK1, EK1C4, and EKL1C, and highlighted their potential application in combating current COVID-19 infection and reinfection, as well as future emerging coronavirus infectious diseases.
Keywords: COVID-19; EK1; coronavirus; fusion inhibitor; heptad repeat 1; lipopeptide.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
S. J., L. L., and S. X. are inventors of some patents related to the SARS‐CoV‐2 fusion inhibitors described in this review. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lan Q, Xia S, Lu L. Coronavirus entry inhibitors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1366:101‐121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

