A Glu-Glu-Tyr Sequence in the Cytoplasmic Tail of the M2 Protein Renders Influenza A Virus Susceptible to Restriction of the Hemagglutinin-M2 Association in Primary Human Macrophages
- PMID: 36098511
- PMCID: PMC9517718
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00716-22
A Glu-Glu-Tyr Sequence in the Cytoplasmic Tail of the M2 Protein Renders Influenza A Virus Susceptible to Restriction of the Hemagglutinin-M2 Association in Primary Human Macrophages
Abstract
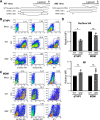
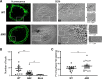
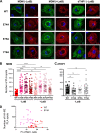
Influenza A virus (IAV) assembly at the plasma membrane is orchestrated by at least five viral components, including hemagglutinin (HA), neuraminidase (NA), matrix (M1), the ion channel M2, and viral ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) complexes, although particle formation is observed with expression of only HA and/or NA. While these five viral components are expressed efficiently in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) upon IAV infection, this cell type does not support efficient HA-M2 association and IAV particle assembly at the plasma membrane. Both defects are specific to MDMs and can be reversed upon disruption of F-actin. However, the relationship between the two defects is unclear. Here, we examined whether M2 contributes to particle assembly in MDMs and if so, which region of M2 determines the susceptibility to the MDM-specific and actin-dependent suppression. An analysis using correlative fluorescence and scanning electron microscopy showed that an M2-deficient virus failed to form budding structures at the cell surface even after F-actin was disrupted, indicating that M2 is essential for virus particle formation at the MDM surface. Notably, proximity ligation analysis revealed that a single amino acid substitution in a Glu-Glu-Tyr sequence (residues 74 to 76) in the M2 cytoplasmic tail allowed the HA-M2 association to occur efficiently even in MDMs with intact actin cytoskeleton. This phenotype did not correlate with known phenotypes of the M2 substitution mutants regarding M1 interaction or vRNP packaging in epithelial cells. Overall, our study identified M2 as a target of MDM-specific restriction of IAV assembly, which requires the Glu-Glu-Tyr sequence in the cytoplasmic tail. IMPORTANCE Human MDMs represent a cell type that is nonpermissive to particle formation of influenza A virus (IAV). We previously showed that close proximity association between viral HA and M2 proteins is blocked in MDMs. However, whether MDMs express a restriction factor against IAV assembly or whether they lack a dependency factor promoting assembly remained unknown. In the current study, we determined that the M2 protein is necessary for particle formation in MDMs but is also a molecular target of the MDM-specific suppression of assembly. Substitutions in the M2 cytoplasmic tail alleviated the block in both the HA-M2 association and particle production in MDMs. These findings suggest that MDMs express dependency factors necessary for assembly but also express a factor(s) that inhibits HA-M2 association and particle formation. High conservation of the M2 sequence rendering the susceptibility to the assembly block highlights the potential for M2 as a target of antiviral strategies.
Keywords: M2; actin cytoskeleton; influenza A virus; macrophage; restriction factor; virus assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

