Volumetric Analysis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Transarterial Chemoembolization and its Impact on Overall Survival
- PMID: 36099102
- PMCID: PMC9463903
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.12964
Volumetric Analysis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Transarterial Chemoembolization and its Impact on Overall Survival
Abstract
Background/aim: To evaluate the prognostic value of Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors (RECIST), modified RECIST and volumetric analysis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treated by transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
Patients and methods: This single-center prospective cohort study included a total of 61 patients with HCC treated by transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). The response of TACE was evaluated on preprocedural and postprocedural CT by two radiologists using RECIST/mRECIST and volumetric response to treatment. Each response assessment method was used to classify the response as progressive disease, stable disease, partial response and complete response. Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank test was performed for each method to evaluate its ability to help predict overall survival and progression free survival. Interobserver variability and reproducibility was determined by the Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients.
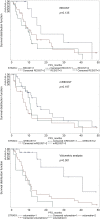
Results: The median overall survival was 17.1 months and the median progression-free survival was 11.1 months. Volumetric assessment was proved to be a prognostic factor for overall survival (p<0.01) and progression-free survival (p<0.001), contrasting with RECIST and mRECIST. All three methods featured very small interobserver variability (p<0.001 for Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients). The patients classified as having stable disease had a 3.8-fold higher risk of death than the patients classified as having a complete/partial response (HR=3.82; 95% Confidence Interval (CI)=1.32-11.02; p=0.013) and a 4.5-fold higher risk of progression (HR=4.46; 95% CI=1.72-11.61; p=0.002).
Conclusion: The prognostic value of volumetric analysis in patients with HCC treated by TACE appears to be superior to RECIST and mRECIST, with a real impact in everyday practice.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; RECIST; mRECIST; transarterial chemoembolization; volumetric analysis.
Copyright © 2022, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors report no conflicts of interest in relation to this study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inter-reader agreement of RECIST and mRECIST criteria for assessing response to transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 May 3;25(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01688-z. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40319244 Free PMC article.
-
Which Criteria Applied in Multi-Phasic CT Can Predict Early Tumor Response in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated Using Conventional TACE: RECIST, mRECIST, EASL or qEASL?Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018 Mar;41(3):433-442. doi: 10.1007/s00270-017-1829-4. Epub 2017 Oct 30. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29086058 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Existing Response Criteria in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Chemoembolization Using a 3D Quantitative Approach.Radiology. 2016 Jan;278(1):275-84. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015142951. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Radiology. 2016. PMID: 26131913 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between SACE (Subjective Angiographic Chemoembolization Endpoint) score and tumor response and its impact on survival after DEB-TACE in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019 Oct;44(10):3463-3479. doi: 10.1007/s00261-019-02128-7. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019. PMID: 31332502
-
RECIST 1.1 versus mRECIST for assessment of tumour response to molecular targeted therapies and disease outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2022 Jun 1;12(6):e052294. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052294. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35649603 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of sorafenib combined with transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Feb 15;17(2):98927. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.98927. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39958535 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Visitation Effect on Quality of Life of Patients Undergoing Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2025 Mar 3;5(2):230-237. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10434. eCollection 2025 Mar-Apr. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2025. PMID: 40034951 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of RANO Criteria for the Assessment of Tumor Progression for Lower-Grade Gliomas.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 21;15(13):3274. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133274. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444384 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
