Effectiveness of Acid-electrolyzed Functional Water for Mouth Wash: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 36099114
- PMCID: PMC9463900
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.12947
Effectiveness of Acid-electrolyzed Functional Water for Mouth Wash: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
Background/aim: Acid-electrolyzed functional water (FW) is an efficient bactericide and gargling with FW might be an effective method of oral care. We investigated the possible use of FW as a mouth wash by an in vitro study.
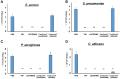
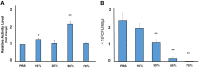
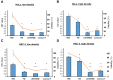
Materials and methods: The bactericidal effect of FW against different species of bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida albicans) was evaluated using the numbers of colony-forming units (CFU). The experiment was conducted using PBS, LISTERINE, and ConCool F (undiluted, and the optimal concentration indicated). To investigate the bactericidal mechanism of FW, the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), an indicator of oxidative action, was measured in S. aureus. FW was diluted with purified water to concentrations of 10, 30, 50, and 70%. The numbers of CFU were measured for each concentration. XTT assays were performed using HSC-3 and HeLa cells, to examine the viability of the cells following treatment with FW. The same experiment was conducted with PBS, LISTERINE, and undiluted ConCool F.
Results: No bacteria treated with FW formed colonies. SOD activity peaked at a 50% concentration of FW and was more than twice that of the control. A significant decrease in the number of CFU was observed following 50% treatment. Since the peaks of the SOD activity and the starting concentrations of the bactericidal effects coincided, the bactericidal effect of FW might be related to its oxidative effects. Bacteria treated with FW had the same survival rate as the other mouth washes.
Conclusion: FW might be clinically applicable as a mouth wash.
Keywords: Acid-electrolyzed functional water; aspiration pneumonia; elderly; mouth wash; oral care.
Copyright © 2022, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors report no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization: Ageing and health. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-andhealth. [Last accessed on March 3, 2022]
-
- GBD 2015 DALYs and HALE Collaborators Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1603–1658. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31460-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaplan V, Angus DC, Griffin MF, Clermont G, Scott Watson R, Linde-Zwirble WT. Hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly: age- and sex-related patterns of care and outcome in the United States. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(6):766–772. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.6.2103038. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
