Renal malakoplakia with invasion of the liver and diaphragm: a patient case and literature review
- PMID: 36100289
- PMCID: PMC9472137
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-251254
Renal malakoplakia with invasion of the liver and diaphragm: a patient case and literature review
Abstract
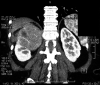
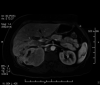
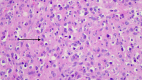
Renal malakoplakia, a seldom seen chronic inflammatory condition, continues to elude medical, surgical, radiological and pathological specialists due to its mimicry of other renal pathologies and low incidence. The variable clinical manifestations and non-specific radiological findings of malakoplakia can be misleading, and ultimately require a pathological diagnosis. A literature review reveals an extremely low prevalence of renal malakoplakia, a handful of invasive renal malakoplakia cases and no reports of liver and diaphragmatic invasion. We present a case of a renal mass with liver and diaphragmatic invasion in a 59-year-old woman that deceived clinicians and radiologists until a pathological diagnosis of renal malakoplakia was performed. This case highlights the need of awareness for malakoplakia in the differential diagnosis for renal invasive and non-invasive masses. The need to await a surgical biopsy and pathological diagnosis is critical to ensure a correct diagnosis and avoid unnecessary surgery of the kidney.
Keywords: Pathology; Radiology; Renal intervention; Urinary tract infections; Urological surgery.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Netto GJ, Amin MB. The lower urinary tract and male genital system. In: Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 2021: 953–83.
-
- Diwakar R, Else J, Wong V. Enlarged kidneys and acute renal failure-why is a renal biopsy necessary for diagnosis and treatment? Nephrol Dial Transplant Off Publ Eur Dial Transpl Assoc - Eur Ren Assoc 2008;23:401–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
