Endocannabinoids at the synapse and beyond: implications for neuropsychiatric disease pathophysiology and treatment
- PMID: 36100658
- PMCID: PMC9700791
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-022-01438-7
Endocannabinoids at the synapse and beyond: implications for neuropsychiatric disease pathophysiology and treatment
Abstract
Endocannabinoids (eCBs) are lipid neuromodulators that suppress neurotransmitter release, reduce postsynaptic excitability, activate astrocyte signaling, and control cellular respiration. Here, we describe canonical and emerging eCB signaling modes and aim to link adaptations in these signaling systems to pathological states. Adaptations in eCB signaling systems have been identified in a variety of biobehavioral and physiological process relevant to neuropsychiatric disease states including stress-related disorders, epilepsy, developmental disorders, obesity, and substance use disorders. These insights have enhanced our understanding of the pathophysiology of neurological and psychiatric disorders and are contributing to the ongoing development of eCB-targeting therapeutics. We suggest future studies aimed at illuminating how adaptations in canonical as well as emerging cellular and synaptic modes of eCB signaling contribute to disease pathophysiology or resilience could further advance these novel treatment approaches.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to American College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
SP is a scientific consultant for Janssen, Psy Therapeutics, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


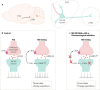

Similar articles
-
Interplay between synaptic endocannabinoid signaling and metaplasticity in neuronal circuit function and dysfunction.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Apr;39(7):1189-201. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12501. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24712998 Review.
-
Synaptic functions of endocannabinoid signaling in health and disease.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 15;124:13-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.06.017. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28625718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty-acid-binding protein 5 controls retrograde endocannabinoid signaling at central glutamate synapses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Mar 27;115(13):3482-3487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721339115. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29531087 Free PMC article.
-
Endocannabinoid signaling and long-term synaptic plasticity.Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:283-306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163149. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19575681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocytes in endocannabinoid signalling.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Oct 19;369(1654):20130599. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0599. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25225093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Anatomy of Synaptic and Extrasynaptic Neurotransmission Between Nociceptive Primary Afferents and Spinal Dorsal Horn Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 6;26(5):2356. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052356. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocannabinoids and related lipids linked to social exclusion in individuals with chronic non-medical prescription opioid use.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Sep;49(10):1630-1639. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01881-8. Epub 2024 May 21. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38773316 Free PMC article.
-
Causes and countermeasures for the increased infection and COVID-19 mortality rates in patients with schizophrenia.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Nov 15;17:456-462. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.11.009. eCollection 2024 Dec. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39634030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Windows of change: Revisiting temporal and molecular dynamics of memory reconsolidation and persistence.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025 Jul;174:106198. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2025.106198. Epub 2025 May 10. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025. PMID: 40354954 Review.
-
Early life stress induces decreased expression of CB1R and FAAH and epigenetic changes in the medial prefrontal cortex of male rats.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Oct 22;18:1474992. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1474992. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39503008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ligresti A, De Petrocellis L, Di Marzo V. From Phytocannabinoids to Cannabinoid Receptors and Endocannabinoids: Pleiotropic Physiological and Pathological Roles Through Complex Pharmacology. Physiol Rev. 2016;96:1593–659. - PubMed
-
- Mechoulam R, Hanus LO, Pertwee R, Howlett AC. Early phytocannabinoid chemistry to endocannabinoids and beyond. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15:757–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

