Recent infection with HCoV-OC43 may be associated with protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 36101832
- PMCID: PMC9458542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105105
Recent infection with HCoV-OC43 may be associated with protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
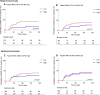
Antibodies against seasonal human coronaviruses (HCoVs) are known to cross-react with SARS-CoV-2, but data on cross-protective effects of prior HCoV infections are conflicting. In a prospective cohort of healthcare workers (HCWs), we studied the association between seasonal HCoV (OC43, HKU1, 229E and NL63) nucleocapsid protein IgG and SARS-CoV-2 infection during the first pandemic wave in the Netherlands (March 2020 - June 2020), by 4-weekly serum sampling. HCW with HCoV-OC43 antibody levels in the highest quartile, were less likely to become SARS-CoV-2 seropositive when compared with those with lower levels (6/32, 18.8%, versus 42/97, 43.3%, respectively: p = 0.019; HR 0.37, 95% CI 0.16-0.88). We found no significant association with HCoV-OC43 spike protein IgG, or with antibodies against other HCoVs. Our results indicate that the high levels of HCoV-OC43-nucleocapsid antibodies, as an indicator of a recent infection, are associated with protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection; this supports and informs efforts to develop pancoronavirus vaccines.
Keywords: Immunology; Molecular physiology; Virology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Aartse A., Eggink D., Claireaux M., van Leeuwen S., Mooij P., Bogers W.M., Sanders R.W., Koopman G., van Gils M.J. Influenza a virus hemagglutinin trimer, head and stem proteins identify and quantify different hemagglutinin-specific b cell subsets in humans. Vaccines. 2021;9:717. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9070717. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson E.M., Goodwin E.C., Verma A., Arevalo C.P., Bolton M.J., Weirick M.E., Gouma S., McAllister C.M., Christensen S.R., Weaver J., et al. Seasonal human coronavirus antibodies are boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 infection but not associated with protection. Cell. 2021;184:1858–1864.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brouwer P.J.M., Brinkkemper M., Maisonnasse P., Dereuddre-Bosquet N., Grobben M., Claireaux M., de Gast M., Marlin R., Chesnais V., Diry S., et al. Two-component spike nanoparticle vaccine protects macaques from SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell. 2021;184:1188–1200.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

