The antitumor activity of hPRDX5 against pancreatic cancer and the possible mechanisms
- PMID: 36102418
- PMCID: PMC9467283
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e12324
The antitumor activity of hPRDX5 against pancreatic cancer and the possible mechanisms
Abstract
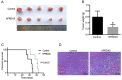
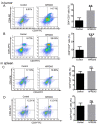
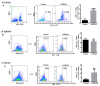
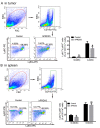
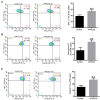
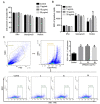
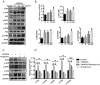
Recombinant human peroxiredoxin-5 (hPRDX5), isolated from anti-cancer bioactive peptide (ACBPs), shows a homology of 89% with goat peroxiredoxin-5 (gPRDX5) and is reported to display anti-tumor activity in vivo. Herein, we explored the effect of hPRDX5 and the responsible mechanism in treating pancreatic cancer. Tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into normal PBS group and treatment group (n=5; 10 mg/kg hPRDX5). Flow cytometry was employed to examine lymphocytes, myeloid-derived suppressor cell subsets, and the function proteins of natural killer (NK) cells in peripheral blood, spleen, and tumor tissues of mice. Western blot was used to measure the protein expressions of the key nodes in TLR4-MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. The rate of tumor suppression was 57.6% at a 10 mg/kg dose in orthotopic transplanted tumor mice. Moreover, the population of CD3+CD4+T cells, NK cells, and CD3+CD8+T cells was significantly increased in the tumor tissue of the hPRDX5 group, while the proportion of granulocytic-myeloid-derived suppressor cells decreased slightly. In addition, after treatment with hPRDX5, the percentage of NK cells in blood increased more than 4-fold. Our findings indicated that hPRDX5 effectively suppressed pancreatic cancer possibly via the TLR4-MAPK-NF-κB signaling cascade; hence hPRDX5 could be a prospective immunotherapy candidate for treating pancreatic cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Bellone G, Turletti A, Artusio E, Mareschi K, Carbone A, Tibaudi D, et al. Tumor-associated transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10 contribute to a systemic Th2 immune phenotype in pancreatic carcinoma patients. Am J Pathol. 1999;155:537–547. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65149-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

