The differential impacts of early detection and accelerated antiretroviral therapy on the epidemiologic trend of sexually acquired HIV infection in Hong Kong
- PMID: 36103496
- PMCID: PMC9473389
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274498
The differential impacts of early detection and accelerated antiretroviral therapy on the epidemiologic trend of sexually acquired HIV infection in Hong Kong
Abstract
Objectives: To assess impacts of early detection and prompt antiretroviral therapy (ART) on the latest epidemiologic situation to inform intervention strategy.
Methods: We analysed data from two clinical cohorts in Hong Kong where sexual transmission accounted for the majority of HIV infections. The two cohorts comprised patients newly diagnosed in 2007-2008 and 2016-2018 respectively. Secular trend and differences between men who have sex with men (MSM) and heterosexual patients were examined. Predictors of late presentation (defined as CD4 ≤350 or AIDS-defining illness within 3 months of diagnosis) and prolonged interval between diagnosis and ART initiation were assessed by multivariable regressions.
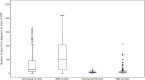
Results: There were 1,136 newly diagnosed HIV patients with 644 in the first and 492 in the second cohort, a majority (91.7%) presented with sexually acquired infection. There were less MSM in the first than the second cohort (50.3%% vs 87.8%, χ2 = 117.05, p<0.001). The mean (SD) number of days between diagnosis and ART initiation decreased from 514.3 (516.1) to 61.8 (94.2) days across the two cohorts. Younger age, non-Chinese, outpatient-based service and lower CD4 count were predictors of faster ART initiation in the first but not in the second cohort. Interval between diagnosis and ART initiation became highly uniform among groups in the second cohort. Nearly 60% were classified as late presenters in both cohorts. Heterosexuals (aOR 1.58, 95% CI 1.13-2.19) had a higher risk of late presentation.
Conclusions: There was remarkable improvement in acceleration of ART initiation. Clinical implementation of accelerated ART recommendations has been effective for both MSM and heterosexuals. Late presentation was more marked among heterosexuals and remained a problem. The continued phenomenon of late presentation could offset the epidemiologic gains from accelerated ART initiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictors of antiretroviral therapy initiation: a cross-sectional study among Chinese HIV-infected men who have sex with men.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Dec 15;15:570. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1309-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26714889 Free PMC article.
-
Late presentations and missed opportunities among newly diagnosed HIV patients presenting to a specialty clinic in Lebanon.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 9;14(1):8296. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55277-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38594292 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretroviral treatment initiation among HIV-positive participants in the Bangkok men who have sex with men cohort study, 2006-2016.Int J STD AIDS. 2021 Jul;32(8):687-693. doi: 10.1177/0956462420985342. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Int J STD AIDS. 2021. PMID: 33629883
-
Simplified clinical algorithm for immediate antiretroviral therapy initiation: The HATI [HIV awal (early) Test & Treat in Indonesia] implementation research in Indonesia.Indian J Med Res. 2022 Jun;156(6):729-741. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_239_23. Indian J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 37056072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Twenty years of clinical human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) in Hong Kong.Hong Kong Med J. 2006 Apr;12(2):133-40. Hong Kong Med J. 2006. PMID: 16603781 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of delay in HIV diagnosis on patient survival: analysis of HIV infection trends from 2007 to 2023.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10412-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39910497 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Electrochemical Sensors in Enhancing HIV Detection.Curr HIV Res. 2025;23(1):2-13. doi: 10.2174/011570162X363311250206045837. Curr HIV Res. 2025. PMID: 39950463 Review.
References
-
- UNAIDS (2014) fast-track ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030.—references—scientific research publishing. [cited 2022Jun20]. https://www.scirp.org/(S(351jmbntvnsjt1aadkposzje))/reference/references...
-
- 90–90–90—an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic [Internet]. UNAIDS. [cited 2021Nov23]. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2017/90-90-90.
-
- Consolidated Guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: Recommendations for a public health approach [Internet]. World Health Organization. World Health Organization; 1970 [cited 2021Nov23]. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/208825. - PubMed
-
- Guidelines—eacsociety [Internet]. [cited 2021Nov23]. https://www.eacsociety.org/media/guidelines_8_0-english_web.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials