A pilot study of neoadjuvant combination of anti-PD-1 camrelizumab and VEGFR2 inhibitor apatinib for locally advanced resectable oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36104359
- PMCID: PMC9472189
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33080-8
A pilot study of neoadjuvant combination of anti-PD-1 camrelizumab and VEGFR2 inhibitor apatinib for locally advanced resectable oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
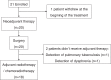
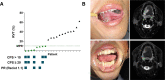
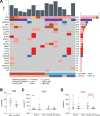
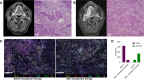
Novel neoadjuvant therapy regimens are warranted for oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). In this phase I trial (NCT04393506), 20 patients with locally advanced resectable OSCC receive three cycles of camrelizumab (200 mg, q2w) and apatinib (250 mg, once daily) before surgery. The primary endpoints are safety and major pathological response (MPR, defined as ≤10% residual viable tumour cells). Secondary endpoints include 2-year survival rate and local recurrence rate (not reported due to inadequate follow-up). Exploratory endpoints are the relationships between PD-L1 combined positive score (CPS, defined as the number of PD-L1-stained cells divided by the total number of viable tumour cells, multiplied by 100) and other immunological and genomic biomarkers and response. Neoadjuvant treatment is well-tolerated, and the MPR rate is 40% (8/20), meeting the primary endpoint. All five patients with CPS ˃10 achieve MPR. Post-hoc analysis show 18-month locoregional recurrence and survival rates of 10.5% (95% CI: 0%-24.3%) and 95% (95% CI: 85.4%-100.0%), respectively. Patients achieving MPR show more CD4+ T-cell infiltration than those without MPR (P = 0.02), and decreased CD31 and ɑ-SMA expression levels are observed after neoadjuvant therapy. In conclusion, neoadjuvant camrelizumab and apatinib is safe and yields a promising MPR rate for OSCC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.X., S.C. and Y.B. are employees of the company 3D Medicines Inc. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhong LP, et al. Randomized phase III trial of induction chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil followed by surgery versus up-front surgery in locally advanced resectable oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:744–751. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.43.8820. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

