Skin permeability prediction with MD simulation sampling spatial and alchemical reaction coordinates
- PMID: 36104960
- PMCID: PMC9674988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.09.009
Skin permeability prediction with MD simulation sampling spatial and alchemical reaction coordinates
Abstract
A molecular-level understanding of skin permeation may rationalize and streamline product development, and improve quality and control, of transdermal and topical drug delivery systems. It may also facilitate toxicity and safety assessment of cosmetics and skin care products. Here, we present new molecular dynamics simulation approaches that make it possible to efficiently sample the free energy and local diffusion coefficient across the skin's barrier structure to predict skin permeability and the effects of chemical penetration enhancers. In particular, we introduce a new approach to use two-dimensional reaction coordinates in the accelerated weight histogram method, where we combine sampling along spatial coordinates with an alchemical perturbation virtual coordinate. We present predicted properties for 20 permeants, and demonstrate how our approach improves correlation with ex vivo/in vitro skin permeation data. For the compounds included in this study, the obtained log KPexp-calc mean square difference was 0.9 cm2 h-2.
Copyright © 2022 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests ERCO Pharma AB has submitted a patent application covering using this lipid barrier model for skin permeability calculations (application no. PCT/EP2017/076,237 and title “skin permeability prediction”). L.N., M.L., and C.W. have stock options in ERCO Pharma AB. M.L. and C.W. are employed by ERCO Pharma AB.
Figures

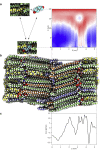
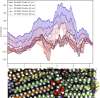
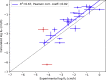
References
-
- Todo H. Transdermal permeation of drugs in various animal species. Pharmaceutics. 2017;9:33. http://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/9/3/33 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buist H., Craig P., Chiusolo A., et al. European Food Safety Authority EFSA Guidance on dermal absorption. EFSA J. 2017;15:4873. https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4873 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jung E.C., Maibach H.I. Animal models for percutaneous absorption: animal models for percutaneous absorption. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015;35:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Degim I., Pugh W., Hadgraft J. Skin permeability data: anomalous results. Int. J. Pharm. X. 1998;170:129–133. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378517398001136
-
- Pecoraro B., Tutone M., et al. Traynor M. Predicting skin permeability by means of computational approaches: reliability and caveats in pharmaceutical studies. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019;59:1759–1771. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00934 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

