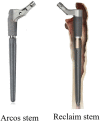
Comparison of two tapered fluted modular titanium (TFMT) stems used in revision hip arthroplasty from a single center
- PMID: 36104996
- PMCID: PMC9465337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2022.08.024
Comparison of two tapered fluted modular titanium (TFMT) stems used in revision hip arthroplasty from a single center
Abstract
Background: TFMT stems are modular porous coated stems widely used in revision hip arthroplasty. Although TFMT stems are popular due to its proven advantage in the setting of severe bone deficiency, subsidence is a concern in these stem designs. We used two TFMT stems between 2013 and 2019, ARCOS(Zimmer Biomet) and Reclaim(Depuy Synthes). We reviewed our results and compared these stems.
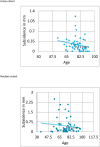
Aim: The primary aim was a) look for early to mid-term stem survival b) radiological outcome measuring subsidence, secondary aim was to measure proximal femoral bone stock changes.
Materials and methods: Data was collected retrospectively. There were 51 patients in Arcos and 57 patients in Reclaim cohort. Both cohorts were comparable with respect to gender, side, BMI, paprosky defect, indications for surgery, ETO and stem length. The mean age group was 78.03 in Arcos and 73.75 in Reclaim.
Results: At a mean follow up of 5 years both cohorts showed excellent stem survival, 96.4% in Reclaim cohort as compared to 100% in Arcos. Subsidence was observed in both but none required a revision due to subsidence. There was a significant difference (p = 0.017) between the cohorts with mean of 2.3 mm(0-12 mm) in Arcos as compared to 4.5 mm(0-25 mm) in Reclaim. Both cohorts showed excellent restoration of proximal femoral bone stock.
Conclusion: Our data shows promising results using TFMT stems at 5 year follow up with more than 95% stem survival, minimal subsidence and good restoration of proximal femoral bone stock. The difference in subsidence between these stems may be attributed to stem geometry and difference in taper.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Hip; Revision hip arthroplasty; Stem taper; TFMT stems.
© 2022 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Ben-Shlomo Y., Blom A., Boulton C., et al. London: National Joint Registry; 2019. The National Joint Registry 16th Annual Report [Internet] Dec. PMID: 32744812. - PubMed
-
- Moreland J.R., Bernstein M.L. Femoral revision hip arthroplasty with uncemented, porous-coated stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;(319):141–150. Oct. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources