Recent advances in ultrasound-controlled fluorescence technology for deep tissue optical imaging
- PMID: 36105171
- PMCID: PMC9463483
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2021.10.002
Recent advances in ultrasound-controlled fluorescence technology for deep tissue optical imaging
Abstract
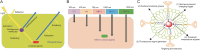
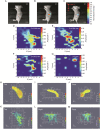
Fluorescence imaging is a noninvasive and dynamic real-time imaging technique; however, it exhibits poor spatial resolution in centimeter-deep tissues because biological tissues are highly scattering media for optical radiation. The recently developed ultrasound-controlled fluorescence (UCF) imaging is a novel imaging technique that can overcome this bottleneck. Previous studies suggest that the effective contrast agent and sensitive imaging system are the two pivotal factors for generating high-resolution UCF images ex vivo and/or in vivo. Here, this review highlights the recent advances (2015-2020) in the design and synthesis of contrast agents and the improvement of imaging systems to realize high-resolution UCF imaging of deep tissues. The imaging performances of various UCF systems, including the signal-to-noise ratio, imaging resolution, and imaging depth, are specifically discussed. In addition, the challenges and prospects are highlighted. With continuously increasing research interest in this field and emerging multidisciplinary applications, UCF imaging with higher spatial resolution and larger imaging depth may be developed shortly, which is expected to have a far-reaching impact on disease surveillance and/or therapy.
Keywords: Deep tissue; High-resolution; Molecular diagnosis; Temperature-sensitive NIR probes; Ultrasound-controlled fluorescence imaging.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Qi J., Sun C., Li D., et al. Aggregation-induced emission luminogen with near-infrared-II excitation and near infrared-I emission for ultra-deep intravital two-photon microscopy. ACS Nano. 2018;12:7936–7945. - PubMed
-
- He S., Song J., Qu J., et al. Crucial breakthrough of second near-infrared biological window fluorophores: Design and synthesis toward multimodal imaging and theranostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018;47:4258–4278. - PubMed
-
- Hemmer E., Benayas A., Legare F., et al. Exploiting the biological windows: Current perspectives on fluorescent bioprobes emitting above 1000 nm. Nanoscale Horiz. 2016;1:168–184. - PubMed
-
- Yu S., Tu D., Lian W., et al. Lanthanide-doped near-infrared II luminescent nanoprobes for bioapplications. Sci. China Mater. 2019;62:1071–1086.
-
- Kim D., Lee N., Park Y., et al. Recent Advances in inorganic nanoparticle-based NIR luminescence imaging: Semiconductor nanoparticles and lanthanide nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017;28:115–123. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

