Medicine-related problems: A recurrent issue among residents living in nursing homes
- PMID: 36105206
- PMCID: PMC9465450
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.978871
Medicine-related problems: A recurrent issue among residents living in nursing homes
Abstract
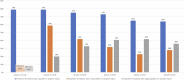
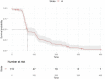
Aim: To examine the incidence and nature of medicine-related problems over time experienced by nursing home residents. Method: We analyzed records collected in the Reducing Medicine-Induced Deterioration and Adverse Events (ReMInDAR) trial. The trial pharmacists provided services to reduce medicine-induced deterioration and adverse reactions for residents every 8-weeks over a year. The problems identified by the pharmacists were documented in reports and subsequently classified independently by research pharmacists using the D.O.C.U.M.E.N.T system. The number and type of problems at each service and time to develop a new problem post first session were assessed. All analyses were performed using R software (Version 4.1.1). Results: The cohort was 115 nursing home residents who received 575 services. In the 12-months, a total of 673 medicine-related problems or symptom reports were identified in 112 residents. Most residents (75%) experienced a new medicine-related problem by the fourth month post the first assessment. After the first session, the proportion of residents with a new medicine-related problem or symptom report declined at each repeated pharmacy session (59% at visit 2 vs. 28% at visit 6, p < 0.01). Conclusion: Residents living in nursing homes frequently experience medicine-related problems. Our results suggest clinical pharmacist services performed every 4-months may have the potential to reduce the medicine-related problems in nursing homes.
Keywords: adverse effects; inappropriate prescribing; long-term care; medication reconciliation; medication therapy management; medicine-related problems; pharmacy services; prescription drug misuse.
Copyright © 2022 Dorj, Lim, Ellett, Kelly, Andrade, Widagdo, Pratt, Bilton and Roughead.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care (2021). Action 4.10 Medication Review. - PubMed
-
- Australian Government-Department for Health (2021). Medicines benefit schedule (MBS): Item 900-903.
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (2020). Health of older people. Canberra: AIHW.
-
- Australian Institute of Health (2012). Residential aged care in Australia 2010-11: A statistical overview.
-
- Cohen J. (1960). A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 20 (1), 37–46. 10.1177/001316446002000104 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources